innodb-java-reader is a java implementation to access MySQL InnoDB storage engine file directly. With the library or command-line tool, it provides read-only features like examining pages, looking up record by primary key, secondary key and generating page heatmap by LSN or filling rate. Innodb-java-reader can be a tool to dump/query table by offloading from MySQL server. Moreover, this project is useful for prototyping and learning MySQL.
InnoDB is a general-purpose storage engine that balances high reliability and high performance in MySQL, since 5.6 InnoDB has become the default MySQL storage engine. In Alibaba, I encountered one performance issue related to MySQL, and this led me to deep dive into InnoDB internal mechanism. To better understand how InnoDB stores data, I introduce this project, and I choose Java language to implement because it is widely used and more understandable. Some of the works are inspired by Jeremy Cole's blog about InnoDB, which helps me a lot.
Currently this project is production-ready and is able to work in real environment.
- Supported MySQL version: 5.6, 5.7, 8.0.
- Make sure InnoDB row format is either
COMPACTorDYNAMIC. - Enable
innodb_file_per_table, which will create standalone*.ibdfile for each table. - InnoDB file page size is set to 16K.
The row format of a table determines how rows are physically stored, which in turn can affect the performance of queries and DML operations. innodb-java-reader supports COMPACT or DYNAMIC page format and can work smartly to choose the right page format decoder to read pages.
innodb-java-reader supports operations like examining pages' information, looking up record by primary key and secondary key, range querying by primary key and secondary key, querying records by page number, dumping table and generating page heatmap & filling rate.
Supported column types are listed below. Java type mapping refer to docs.
| Type | Support column types |
|---|---|
| Numeric | TINYINT, SMALLINT, MEDIUMINT, INT, BIGINT, FLOAT, REAL, DOUBLE, DECIMAL, NUMERIC |
| String and Binary | CHAR, VARCHAR, BINARY, VARBINARY, TINYBLOB, BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, LONGBLOB, TINYTEXT, TEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, LONGTEXT |
| Date and Time | DATETIME, TIMESTAMP, TIME (support precision), YEAR, DATE |
| Other | BOOL, BOOLEAN, ENUM, SET, BIT |
Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.database</groupId>
<artifactId>innodb-java-reader</artifactId>
<version>1.0.10</version>
</dependency>
To use snapshot version, please refer to this doc.
Here's an example to look up record in a table by primary key.
String createTableSql = "CREATE TABLE t (id int(11), a bigint(20)) ENGINE=InnoDB;";
String ibdFilePath = "/usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd";
try (TableReader reader = new TableReaderImpl(ibdFilePath, createTableSql)) {
reader.open();
GenericRecord record = reader.queryByPrimaryKey(ImmutableList.of(4));
Object[] values = record.getValues();
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(values));
}
More usage you can jump to API usage section. The best place to better explore is to look at the examples for some common use cases addressed here in innodb-java-reader-demo.
Here's an example to dump all records with command-line tool.
You can download latest version of innodb-java-reader-cli.jar from release page or build from source.
t.ibd is the InnoDB ibd file path. t.sql is where the output of SHOW CREATE TABLE <table_name> saved as content, you can generate table definitions by executing mysqldump -d -u<username> -p<password> -h <hostname> <dbname> in command-line.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c query-all -o output.dat
The result is the same by running mysql -N -uroot -e "select * from test.t" > output.
But to be aware that if pages are not flushed from InnoDB Buffer pool to disk, then the result maybe not consistent. How long do dirty pages usually stay dirty in memory? That is a tough question, InnoDB leverages WAL in terms of performance, so there is no command available to flush all dirty pages. Only internal mechanism controls when there need pages to flush, like Page Cleaner thread, adaptive flushing, etc.
Here's another example to generate heatmap.
Assume we have a table without secondary index, and the primary key is built by inserting rows in key order. Then run the following command.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c gen-lsn-heatmap -args ./out.html
The heatmap shows as below.
The pages are allocated and filled perfectly as color changes from blue (LSN is smallest) to red (LSN is biggest), from the beginning of the file towards to the end.
More usage you can jump to Command-line tool section.
You can prepare some data beforehand. All the following examples will be based on a table named t.
CREATE TABLE `t`
(`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`a` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`b` varchar(64) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB;
delimiter ;;
drop procedure if EXISTS idata;
create procedure idata()
begin
declare i int;
set i=1;
while(i<=5)do
insert into t values(i, i * 2, REPEAT(char(97+((i - 1) % 26)), 8));
set i=i+1;
end while;
end;;
delimiter ;
call idata();
After creating and populating the very simple table, there should be 5 rows.
mysql> select * from t;
+----+----+----------+
| id | a | b |
+----+----+----------+
| 1 | 2 | aaaaaaaa |
| 2 | 4 | bbbbbbbb |
| 3 | 6 | cccccccc |
| 4 | 8 | dddddddd |
| 5 | 10 | eeeeeeee |
+----+----+----------+
There are two ways to specify a table definition, or TableDef within the library.
Run SHOW CREATE TABLE statement in MySQL command-line and copy the output as a string. Inside innodb-java-reader, it leverages JSqlParser and antlr4 to parse SQL to AST and get the table definition.
You can generate all table definitions by executing mysqldump -d -u<username> -p<password> -h <hostname> <dbname> in command-line.
For example,
String createTableSql = "CREATE TABLE `t`\n"
+ "(`id` int(11) NOT NULL ,\n"
+ "`a` bigint(20) NOT NULL,\n"
+ "`b` varchar(64) NOT NULL,\n"
+ "PRIMARY KEY (`id`))\n"
+ "ENGINE=InnoDB;";
Create a TableDef instance with all Columns. Column can be created in fluent style by setting the required column name, type, while there are optional settings to specify nullable, charset or if the column is primary key.
For variable-length or fixed-length column types like VARCHAR, VARBINARY, CHAR, column type can be declared with a length that indicates the maximum length you want to store, just like what you define a DDL in MySQL. For integer types, the display width of the integer column will be ignored.
For example, to create table with single primary key.
TableDef tableDef = new TableDef().setDefaultCharset("utf8mb4")
.addColumn(new Column().setName("id").setType("int(11)").setNullable(false).setPrimaryKey(true))
.addColumn(new Column().setName("a").setType("bigint(20)").setNullable(false))
.addColumn(new Column().setName("b").setType("varchar(64)").setNullable(false))
.addColumn(new Column().setName("c").setType("varchar(1024)").setNullable(true));
To create table with multiple column primary key.
TableDef tableDef = new TableDef()
.setDefaultCharset("utf8mb4")
.addColumn(new Column().setName("id").setType("int(11)").setNullable(false)
.addColumn(new Column().setName("a").setType("bigint(20)").setNullable(false))
.addColumn(new Column().setName("b").setType("varchar(64)").setNullable(false))
.addColumn(new Column().setName("c").setType("varchar(1024)").setNullable(true))
.setPrimaryKeyColumns(ImmutableList.of("a", "b"));
Table without primary key is also supported. By default, a 6 bytes ROW ID will be treated as primary key.
Thread-safe class TableReader enables you to call all the useful APIs.
With try-with-resources statement, you can ensure that IO resource used by TableReader is closed at the end of all invocations. By default, TableReader leverage buffer IO, pages are read from page cache into DirectByteBuffer and then copy to heap to manage their lifecycle. This framework is also open for extension to use mmap or direct io.
There are two constructors, one needs to provide tablespace file *.ibd file path and create table sql, while the other needs the *.ibd file path and TableDef.
For example,
String createTableSql = "CREATE TABLE `tb11`\n"
+ "(`id` int(11) NOT NULL ,\n"
+ "`a` bigint(20) NOT NULL,\n"
+ "`b` varchar(64) NOT NULL,\n"
+ "PRIMARY KEY (`id`))\n"
+ "ENGINE=InnoDB;";
String ibdFilePath = "/usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd";
try (TableReader reader = new TableReaderImpl(ibdFilePath, createTableSql)) {
reader.open();
// API invocation goes here...
}
Moreover, there is a useful factory utility which can facilitate the process of creating TableReader. In this case, table definition is no longer needed, so you can skip table definition using SQL or API as section 5.1 describes.
For example,
String createTableSql = "CREATE TABLE `tb11`\n"
+ "(`id` int(11) NOT NULL ,\n"
+ "`a` bigint(20) NOT NULL,\n"
+ "`b` varchar(64) NOT NULL,\n"
+ "PRIMARY KEY (`id`))\n"
+ "ENGINE=InnoDB;";
TableDefProvider tableDefProvider = new SqlTableDefProvider(createTableSql);
TableReaderFactory tableReaderFactory = TableReaderFactory.builder()
.withProvider(tableDefProvider)
.withDataFileBasePath("/usr/local/mysql/data/test/")
.build();
TableReader reader = tableReaderFactory.createTableReader("tb11");
try {
reader.open();
// API invocation goes here...
} finally {
reader.close();
}
You can also provide a sql file path, the file
contains multiple SQLs, the table name should match the ibd file name, or else the tool is not able to
identify the ibd file to read, you can generate the file by executing mysqldump -d -u<username> -p<password> -h <hostname> <dbname> in command-line.
TableDefProvider tableDefProvider = new SqlFileTableDefProvider("/path/mysqldump_ddl.sql");
TableReaderFactory tableReaderFactory = TableReaderFactory.builder()
.withProvider(tableDefProvider)
.withDataFileBasePath("/usr/local/mysql/data/test/")
.build();
TableReader reader = tableReaderFactory.createTableReader("t");
try {
reader.open();
// API invocation goes here...
} finally {
reader.close();
}
The provider is extensible, in the future, we plan to support MysqlFrmTableDefProvider as well.
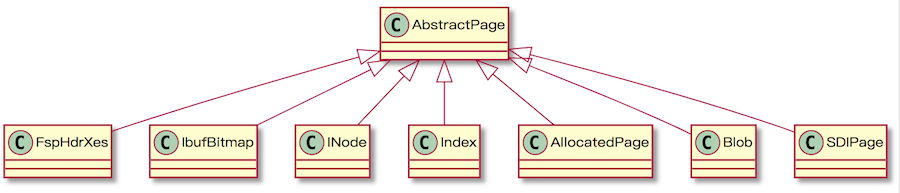
This will give you a high-level overview about InnoDB file structure, as it results in a list of AbstractPage, for example, you can get all contiguous pages of their basic information.
try (TableReader reader = new TableReaderImpl(ibdFilePath, createTableSql)) {
reader.open();
long numOfPages = reader.getNumOfPages();
List<AbstractPage> pages = reader.readAllPages();
}
AbstractPage is the parent class of all pages. The page definition can be found in fil0fil.h. innodb-java-reader supports some of the commonly used page types like FspHdr/Xdes page, insert buffer bitmap page, index page, blob page, SDI page (only in MySQL 8.0 or later) and allocated page (unused page).
AbstractPage base class includes 38 bytes FilHeader and 8 bytes FilTrailer for all page type. The raw byte array body will be extracted accordingly for sub-classes. You can find the APIs regarding how to access the detailed structure for different types under page package in Javadoc.
For example, the demo table t will result as below.
0,FILE_SPACE_HEADER,numPagesUsed=4,size=6,xdes.size=1
1,IBUF_BITMAP
2,INODE,inode.size=2
3,INDEX
4,ALLOCATED
5,ALLOCATED
Moreover, Iterator<AbstractPage> getPageIterator() is useful to get pages iteratively.
You can query page one by one. For supported page types, you can check the internal information.
try (TableReader reader = new TableReaderImpl(ibdFilePath, createTableSql)) {
reader.open();
AbstractPage page = reader.readPage(3);
}
This will walk through the B+ tree index in ascending order, you can take it as a full-table scan operation as well. First it locates to the root page of the primary key, and do a depth-first traversal recursively, along the traversal it will collects all the records.
try (TableReader reader = new TableReaderImpl(ibdFilePath, createTableSql)) {
reader.open();
List<GenericRecord> recordList = reader.queryAll();
for (GenericRecord record : recordList) {
Object[] values = record.getValues();
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(values));
assert record.getPrimaryKey() == record.get("id");
}
}
output result as blow.
[1, 2, aaaaaaaa]
[2, 4, bbbbbbbb]
[3, 6, cccccccc]
[4, 8, dddddddd]
[5, 10, eeeeeeee]
GenericRecord represents one row.
- To retrieve a column data through column name, you can invoke
Object get(String columnName). - To retrieve a column data by column index, you can invoke
Object get(int index). - To retrieve the primary key, you can invoke
Object getPrimaryKey().
queryAll accepts an optional argument Predicate<Record> to filter.
This feature enables you to dump data if data persists in InnoDB file by offloading MySQL.
This only works for index page type.
try (TableReader reader = new TableReaderImpl(ibdFilePath, createTableSql)) {
reader.open();
List<GenericRecord> recordList = reader.queryByPageNumber(3);
}
For leaf B+ tree page, the result record will be rows of a table.
For non-leaf page in multi-level B+ tree index, the result record will be the primary with all the other columns as NULL. You can check whether it is leaf or not and get the child page number in clustered index.
if (!record.isLeafRecord()) {
System.out.println(record.getChildPageNumber());
}
B+ tree is an efficient data structure to do point and range query, it requires limited number of disk IO operations even for a very large table since the depth of the tree is usually not very big, that is why B+ tree scales nicely.
To look up record by primary key, innodb-java-reader will start from the root page in clustered index and do point-query in B+ tree index.
If the page is leaf, then it will do binary search in page directory slots to locate the nearest record (the highest key that smaller than the target key, innodb-java-reader leverages search-insertion-position for sorted array algorithm to do that), and walk through the records one by one as they are singly linked in one page until the target value found or return null if not present.
For non-leaf page, the record is simply the child page number, so innodb-java-reader will go deeper in the multiple-level B+ tree to the child page and run recursively.
Primary key parameter is a list of objects, single column primary key (list size will be 1) and multiple column primary key are supported.
try (TableReader reader = new TableReaderImpl(ibdFilePath, createTableSql)) {
reader.open();
GenericRecord record = reader.queryByPrimaryKey(ImmutableList.of(4));
Object[] values = record.getValues();
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(values));
assert record.getPrimaryKey() == record.get("id");
System.out.println("id=" + record.get("id"));
System.out.println("a=" + record.get("a"));
}
Note that in MySQL 5.7 or earlier version, usually page 3 will be the root page of the clustered index, page 4 will be the root of the first secondary key, etc. After MySQL 8.0 or later, page 3 is usually the SDI page with data dictionary, and root page will usually go next to page 4. innodb-java-reader assumes the root page is either page 3 or 4 and can work smartly to determine where to start.
rangeQueryByPrimaryKey method requires at least 4 arguments: lower key, lower operator, upper key and upper operator. Operators include >, >=, <, <= and nop (works on unlimited bound).
MySQL InnoDB engine will have its own way to execute a range query, here in innodb-java-reader, it will use a naive and simple way: go deep into the leaf node of B+ tree index, and visit page by page, record by record, the algorithm looks like below:
- Lookup the record greater than or equal to the lower bound target key.
- Lookup the record smaller than the upper bound target key.
- Start from the record found in step 1, go ahead by the singly linked record pointer to visit each record next until
SUPREMUMrecord found, which mean the end of the page has met. - There are pointers stored in the
FilHeader, point to the logical previous and next page. Go to the next page and query all records from theINFINIMUMrecord. Repeat the process in step 3. If the page is where the record smaller than the upper bound target key resides, then it will compare record read with the target end key, so that we can exit nicely.
For example, the lower and upper bound target key can be empty list, which means no limit is specified.
try (TableReader reader = new TableReaderImpl(ibdFilePath, createTableSql)) {
reader.open();
List<GenericRecord> recordList = reader.rangeQueryByPrimaryKey(
ImmutableList.of(5), ComparisonOperator.GT,
ImmutableList.of(8), ComparisonOperator.LT);
recordList = reader.rangeQueryByPrimaryKey(null, null);
recordList = reader.rangeQueryByPrimaryKey(5, null);
}
rangeQueryByPrimaryKey accepts an optional argument Predicate<Record> to filter and List<String> to project selected columns.
For extremely large tablespace, querying like queryAll or rangeQueryByPrimaryKey would cause out of memory error since data cannot fit into memory. The iterator pattern will help you out, it will load page by page until you really visit these records.
For example, getQueryAllIterator will return an iterator to visit all records.
try (TableReader reader = new TableReaderImpl(ibdFilePath, createTableSql)) {
reader.open();
Iterator<GenericRecord> iterator = reader.getQueryAllIterator();
int count = 0;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
GenericRecord record = iterator.next();
Object[] values = record.getValues();
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(values));
count++;
}
System.out.println(count);
}
For example, getRangeQueryIterator will return an iterator to visit targeted records based on the lower and upper bound just like what rangeQueryByPrimaryKey does.
try (TableReader reader = new TableReaderImpl(ibdFilePath, createTableSql)) {
reader.open();
Iterator<GenericRecord> iterator = reader.getRangeQueryIterator(
ImmutableList.of(5), ComparisonOperator.GTE,
ImmutableList.of(8), ComparisonOperator.LTE);
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
GenericRecord record = iterator.next();
Object[] values = record.getValues();
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(values));
}
}
getRecordIteratorBySk will return an iterator to scan table by secondary key, the order will be the same as in secondary key.
try (TableReader reader = new TableReaderImpl(ibdFilePath, createTableSql)) {
reader.open();
Iterator<GenericRecord> iterator = reader.getRecordIteratorBySk("key_a",
ImmutableList.of(2L), ComparisonOperator.GTE,
ImmutableList.of(9L), ComparisonOperator.LT);
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
GenericRecord record = iterator.next();
Object[] values = record.getValues();
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(values));
}
}
Projection and ordering work as below. Covering index is supported, it skips the operation to look up record back to clustered key (primary key), which will usually be more performant.
boolean isAsc = false;
Iterator<GenericRecord> iterator = reader.getRecordIteratorBySk("key_a",
ImmutableList.of(6L), ComparisonOperator.GTE,
null, ComparisonOperator.NOP,
ImmutableList.of("id", "a", "b"), isAsc);
Note that if table has ever been altered to add or remove indices, the secondary key root page number may be incorrect, and cause error, please goes to FAQ.
Filtering works on queryAll and rangeQueryByPrimaryKey, this is more likely index condition pushdown.
Projection works for almost all APIs, for example.
// range query with projection
List<GenericRecord> recordList = reader.rangeQueryByPrimaryKey(
ImmutableList.of(5), ComparisonOperator.GT,
ImmutableList.of(8), ComparisonOperator.LT,
ImmutableList.of("a"));
// range query with no limit, equivalent to query all, with projection
Iterator<GenericRecord> iterator = reader.getRangeQueryIterator(
null, ComparisonOperator.NOP,
null, ComparisonOperator.NOP,
ImmutableList.of("a"));
Ordering works on getQueryAllIterator and getRangeQueryIterator, for example.
boolean ascOrder = false;
reader.getRangeQueryIterator(
ImmutableList.of(2), ComparisonOperator.GTE,
ImmutableList.of(5), ComparisonOperator.LT,
ascOrder);
You can download latest version of innodb-java-reader-cli.jar from release page or build from source.
Usage shows as below.
usage: java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar [-args <arg>] [-c <arg>]
[-delimiter <arg>] [-desc] [-h] [-i <arg>] [-iomode <arg>] [-json]
[-jsonpretty] [-nullstring <arg>] [-o <arg>] [-projection <arg>]
[-quotemode <arg>] [-s <arg>] [-showheader] [-skname <arg>]
[-skordinal <arg>] [-skrootpage <arg>]
-args <arg> arguments
-c,--command <arg> mandatory. command to run, valid
commands are:
show-all-pages,show-pages,query-b
y-page-number,query-by-pk,query-b
y-sk,query-all,range-query-by-pk,
gen-lsn-heatmap,gen-filling-rate-
heatmap,get-all-index-page-fillin
g-rate
-delimiter,--delimiter <arg> field delimiter, default is tab
-desc,--desc if records sorted in descending
order, works for query all and
range query
-h,--help usage
-i,--ibd-file-path <arg> mandatory. innodb file path with
suffix of .ibd
-iomode,--output-io-mode <arg> output io mode, valid modes are:
buffer,mmap,direct
-json,--json-style set to true if you would like to
show page info in json format
style
-jsonpretty,--json-pretty-style set to true if you would like to
show page info in json pretty
format style
-nullstring,--null-string <arg> null value string, default is
"null"
-o,--output <arg> save result to file instead of
console, the argument is the file
path
-projection,--projection <arg> projection list with column names
delimited by comma
-quotemode,--quote-mode <arg> value quote mode, valid modes
are: all,nonnull,nonnumeric,none,
default is none
-s,--create-table-sql-file-path <arg> create table sql file path, the
sql is DDL as SHOW CREATE TABLE
<table_name>, the file can
contain multiple SQLs, the table
name should match the ibd file
name, or else the tool is not
able to identify the ibd file to
read, you can generate the file
by executing mysqldump -d
-u<username> -p<password> -h
<hostname> <dbname>` in
command-line.
-showheader,--show-header set to true if you want to show
table header when dumping table
-skname,--skname <arg> secondary key name
-skordinal,--skordinal <arg> secondary key ordinal in DDL
-skrootpage,--skrootpage <arg> secondary key root page number
You can customize log4j configuration by adding -Dlog4j.configuration=file:/path/log4j.properties in command.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c show-all-pages
Output:
=====page number, page type, other info=====
0,FILE_SPACE_HEADER,space=141,numPagesUsed=4,size=6,xdes.size=1
1,IBUF_BITMAP
2,INODE,inode.size=2
3,INDEX,root.page=true,index.id=176,level=0,numOfRecs=5,num.dir.slot=2,garbage.space=0
4,ALLOCATED
5,ALLOCATED
Arguments are page numbers, separated by comma.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c show-pages -args "3,4,5"
ToString method will be invoked for every page examined and print on console. You can add --json-style or --json-pretty-style to print out information in more human readable way.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c query-all
The result is the same as mysql -N -uroot -e "select * from test.t" > output.dat
Field is delimited by tab, you can specify -delimiter "," to use comma as delimiter.
Argument is page number, the results is all the records within the page, only index page type is supported.
For B+tree non-leaf page, the records are keys only, for leaf page, the records are full tuples.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c query-by-page-number -args 3
Argument is the target key.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c query-by-pk -args 5
For composite primary key, fields will be delimited by ,, you can change the delimiter by applying -Dinnodb.java.reader.composite.key.delimiter or setting environment.
For example,
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c query-by-pk -args abc,123,bcd
Arguments are lower operator;lower bound;upper operator;upper bound separated by ;.
Operators include >, >=, <, <= and nop (works on unlimited bound).
You can change delimiter by -Dinnodb.java.reader.range.query.key.delimiter or set environment.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c range-query-by-pk -args ">=;1;<;3"
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c range-query-by-pk -args ">=;1;nop;null" // no upper limit
For composite key, args will like >;abc,123,bcd;<;xyz,5,jkl or >;abc,123,bcd;<;xyz,5,null.
Argument is like "Range querying by primary key", you should provide the key name. For example, the following command result will be the same as "SELECT * FROM t WHERE a = 1";
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c query-by-sk -args ">=;1;<=;1" -skname "key_a"
You can use command-line tool to dump data, but dirty pages might not be flushed to disk, so the data consistency is what you must consider. You can dump records by query-all or range-query-by-pk like below.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c query-all -o output.dat
The output.dat file contains record per line with tab delimited for fields.
The result is the same as mysql -N -uroot -e "select * from test.t" > output.dat
By default, dumping data will use mmap to write to file, you can specify -iomode buffer or -iomode direct as well. Note if no -o is used, system IO redirect is not efficient.
Arguments are the output html file path, the heatmap width and height.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c gen-lsn-heatmap -args "./out.html 800 1000"
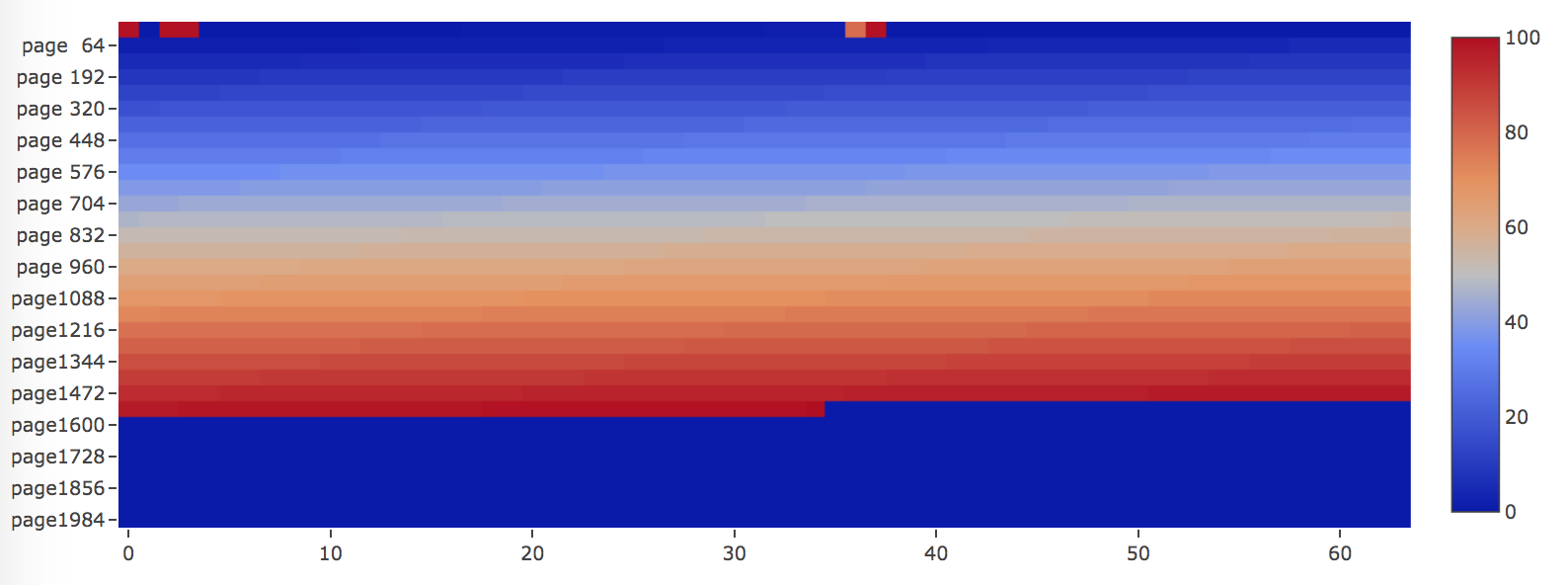
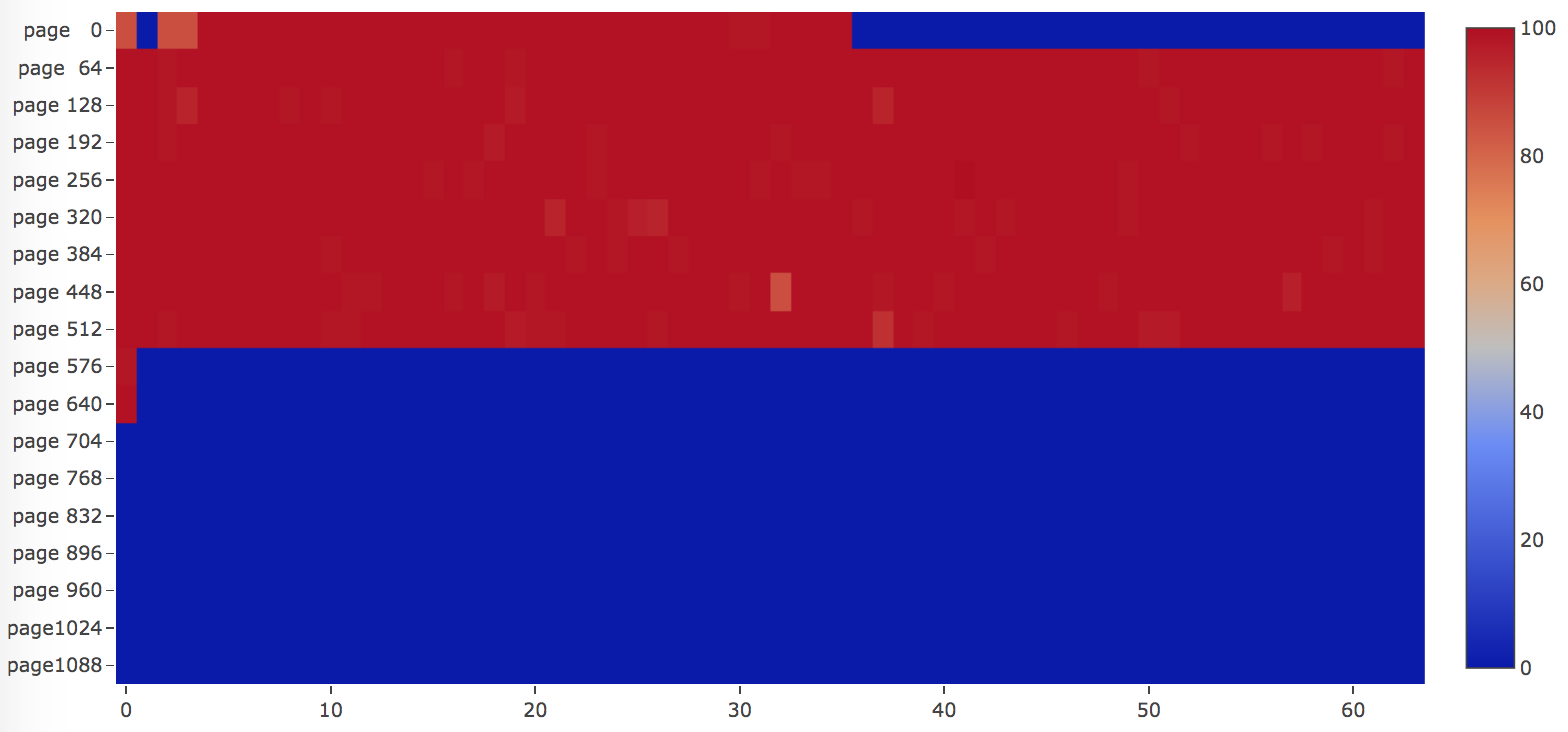
Here is an example if we have a table with random primary key insertion order. Then many pages will be revisited, as illustrated in the image below, most of the pages are "red" colored, which means those pages LSN are close to each other.
Another example will be a table with two indices, one is primary key built by inserting rows in key order, the other is a secondary key with random insertion order. As you can see, the primary key index is written to in ascending order as they are visited from the beginning of the file until the end. Pages of the secondary keys are "red" colored, which means those pages LSN are close to each other.
Arguments are the output html file path, the heatmap width and height.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c gen-filling-rate-heatmap -args "./out.html 800 1000"
Filling rate, also known as page filling factor, means how efficient for InnoDB to make use of storage space. InnoDB store records in row-oriented layout, usually this is good for OLTP scenario. While in big data industry, columnar storage format is more preferred, because for performance, it can read required data, skip unnecessary deserialization, leverage specific encoding and better for compression, so the storage space is much more saved. Although, row-oriented format is not friendly in term of file size, we still want to know the space occupied by data, InnoDB file can be fragmented due to logical deletion or B+ tree splitting. Filling rate for every page is calculated by examining used space / page size, used space equals to heap_top_position + page_directory_slots_bytes + FilTrailer - garbage_space. This is different from data_free value when you examine a table through information_schema.TABLES, data_free means the space allocated on disk for, but not used.
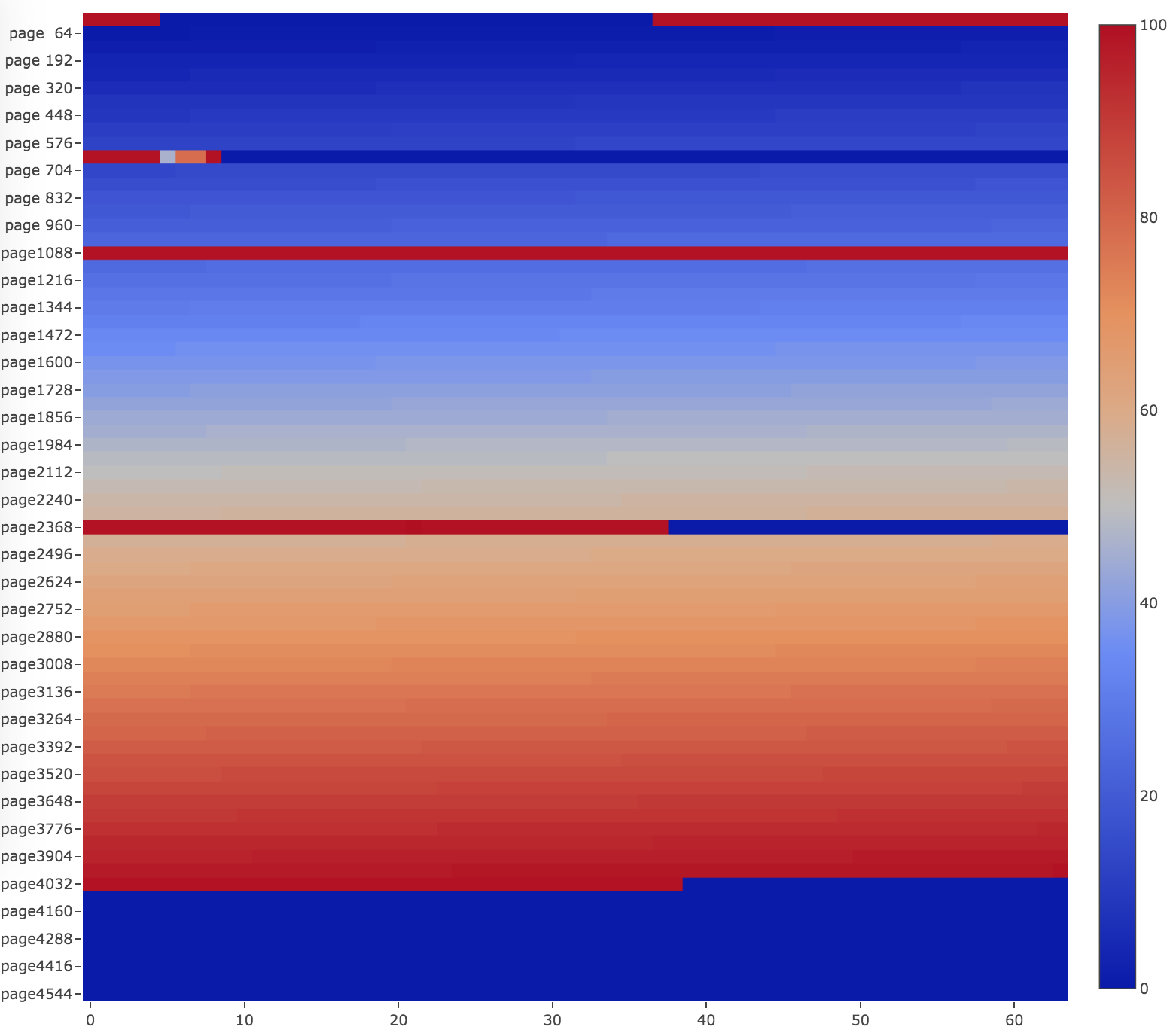
Assume we build a table by inserting rows in sequential order. The page filling rate will be more than 90 percent initially.
After deleting some rows. Looking at the filling rate heatmap, we can see some pages are fragmented and the filling rate drops dramatically.
After OPTIMIZED TABLE <T>, the table filling rate will go back to more than 90 percent.
java -jar innodb-java-reader-cli.jar \
-ibd-file-path /usr/local/mysql/data/test/t.ibd \
-create-table-sql-file-path t.sql \
-c get-all-index-page-filling-rate
innodb-java-reader is a standard Maven project. Simply run the following command from the project root directory, make sure all unit testcases are passed.
mvn clean install
Use the executable jar innodb-java-reader-cli/target/innodb-java-reader-cli.jar to run command.
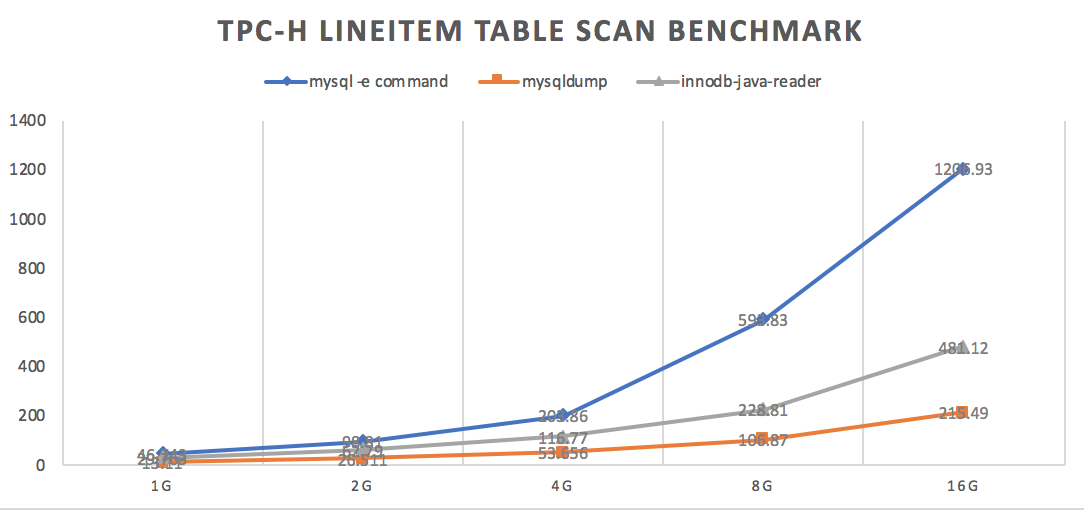
For benchmark of innodb-java-reader, mysql -e "select.." > output and mysqldump, please visit here.
TPC-H LINEITEM table scan result is as below.
- Support MySQL 8.0 newly introduced LOB page.
- Load table metadata from system tablespace.
- Support compressed table.