SQL stands for Structured Query Language. SQL will allow you to interact with the data stored in a database.
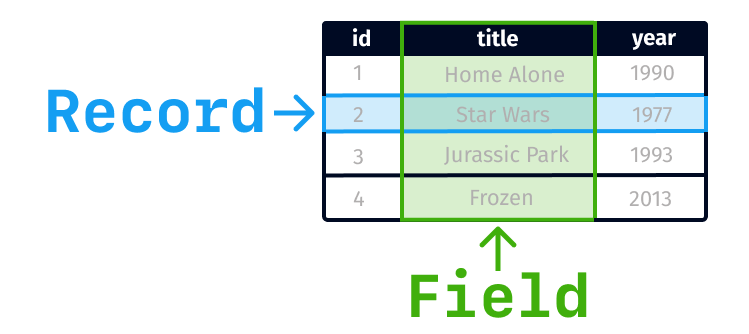
Each database has at least one table, and each table has records (rows) amd fields (columns).
A schema is a visual representation of how a database is organized, showing its tables, fields and keys.
The name of the fields on the first row are called header and the corresponding row is called the header row.
We have a table named tb. It has fields f1, f2 and f3. The data stored in the field f2 can be accessed through:
SELECT f2
FROM tbMultiple fields can be selected by separating the field with commas.
SELECT f2, f3
FROM tbThe * symbol allows you to select all the fields in a table.
The term for a request of information from a database is query.
Data that can be stored in tables is called structured data.
Unstructured data is information that is difficult to store in tables.
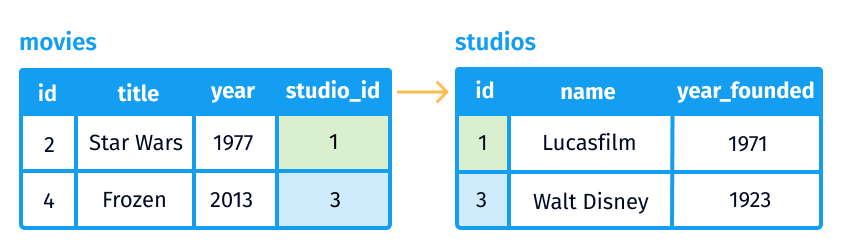
A relational database stores information in tables. The different tables in a relational database are connected to each other using fields which are called keys.
In an SQL query, -- can be used to write comments.
Block comments can be opened using /* and closed using */.
Data professionals use uppercase for the SQL command words and lowercase for tables and fields names.
The data can be sorted according to the values in a field by adding the following line after the name of the table:
ORDER BY f2The extracted data will be sorted in ascending order by default. The keywords ASC and DESC should be added after the name of the field.
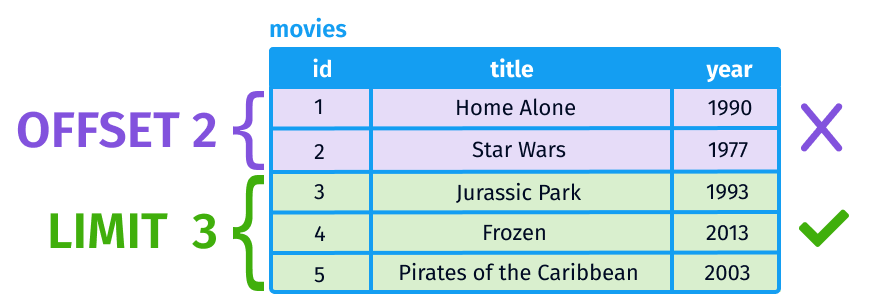
The LIMIT keyword can be used to limit the number of the records, followed by an integer.
Note
The correct sequence of ordering and limiting the number of extracted records is ORDER and then LIMIT.
The OFFSET keyword should be added after the value of the LIMIT keyword, followed by an integer. For example:
LIMIT 3 OFFSET 2Data types can be string, numerical, boolean (True/False) and date/time.
The values in some fields of a table can be manipulated and be assigned to a newly defined field. For example:
SELECT f1, f2+f3 AS TOTAL
FROM tbThe operators + and *
Text data can be merged using the CONCAT function. For instance:
SELECT CONCAT(f1, f2) AS merged
FROM tbA condition can be applied on the data using the WHERE keyword. Values in a field can be filtered by the following line:
WHERE f2 = 'value'Note
Strings should be surrounded with quotation marks.
The example above can be applied to text data. For numeric data, the comparison operators >, >=, <, <=, = and <> (not equal) can be used. The <> operator can also be used for string data.
The LIKE keyword is used with the WHERE command to search for patterns in string values. It can be put where the mathematical operators are used.
The % special symbol is known as a wildcard and is used to create patterns. For example,
WHERE email LIKE '%@gmail.com'returns the emails ending with @gmail.com.
The underscore symbol _ is another wildcard and represents 1 single character only.
Multiple queries can be separated using ; at the end of the last line of each query.
Strings in a field can be uppercased or lowercased using the functions LOWER() and UPPER(), respectively.
SELECT LOWER(f2), UPPER(f3)
FROM tbTip
The LOWER can be used to perform a not case-insensitive search using a pattern in lowercase.
The maximum value can be obtained using the MAX() function, and MIN() for the minimum.
SELECT MAX(f2)
FROM tb;
SELECT MIN(f2)
FROM tb;Note
All of the following aggregation operations can be performed in the same manner.
COUNT() counts the number of records
SUM() produces the total sum of the values in a numerical field.
AVG() calculates the average value.
Note
When running queries that involve different operations, filtering happens first.
Servers are computers that are always listening for requests of information. You can request information from a database server through an API (Application Programming Interface).
Web scraping allows you to extract information from websites.
GROUP BY allows you to organize similar data into categories. It's combined with aggregations to compute key metrics for a group of records.
SELECT f1, AVG(f2)
FROM tb
GROUP BY f1Note
When a query contains both WHERE and GROUP BY, data is filtered first, then grouped.
HAVING allows you to filter data that has been grouped.
Note
When a query contains both GROUP BY and HAVING, data is grouped first, then filtered.
The duplicated records can be identified using the following query:
SELECT f1, COUNT(f1)
FROM tb
GROUP BY f1
HAVING COUNT(f1) > 1;Use DISTINCT to eliminate duplicate values.
SELECT DISTINCT f1
FROM tbNULL is used to indicate that a data value is missing and does not exist in the database. NULL values are not shown in result tables.
Use IS NULL in combination with WHERE to find missing values.
SELECT *
FROM tb
WHERE f2 IS NULLExtract non-null values using IS NOT NULL.
SELECT *
FROM tb
WHERE f2 IS NOT NULLOperations involving boolean values are known as logical operations.
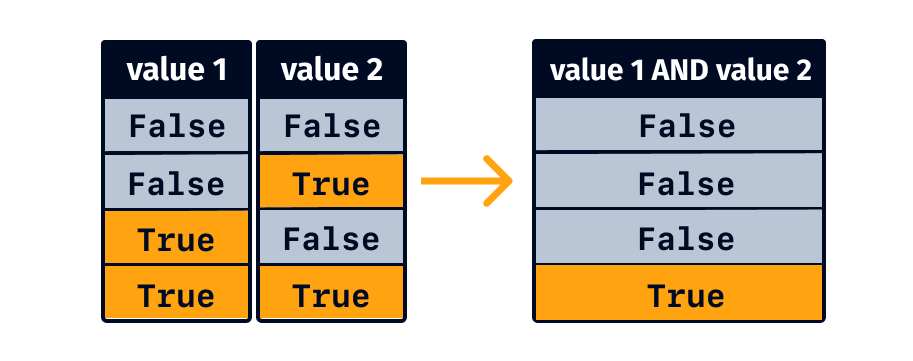
The AND operation results in a True value only when all the values are True at the same time.
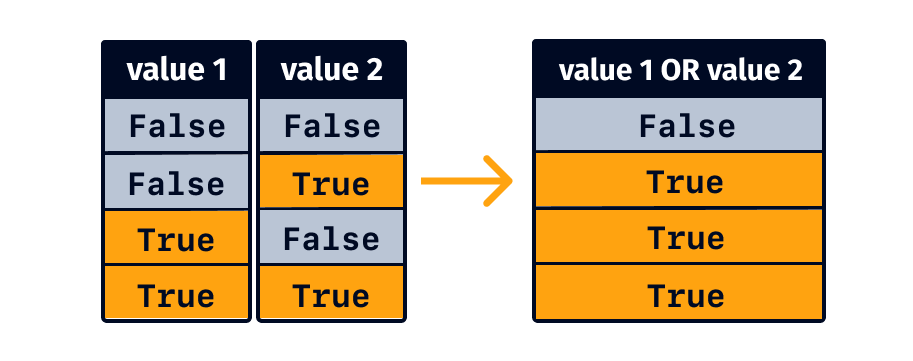
The OR logical operation results in a True value if at least one of the conditions is True.