LTP Next-Gen runner is a new version of the runltp script used by the
Linux Test Project.
Host information
System: Linux
Node: susy
Kernel Release: 5.14.21-150400.24.33-default
Kernel Version: #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Fri Nov 4 13:55:06 UTC 2022 (76cfe60)
Machine Architecture: x86_64
Processor: x86_64
Temporary directory: /tmp/runltp.acer/tmpcwtket0m
Connecting to SUT: host
Downloading suite: math
Starting suite: math
abs01: pass | tained (0.005s)
atof01: pass | tained (0.005s)
float_bessel: pass | tained (0.702s)
float_exp_log: pass | tained (0.703s)
float_iperb: pass | tained (0.288s)
float_power: pass | tained (0.540s)
float_trigo: pass | tained (0.643s)
fptest01: pass | tained (0.020s)
fptest02: pass | tained (0.005s)
nextafter01: pass | tained (0.004s)
Suite Name: math
Total Run: 10
Elapsed Time: 2.9 seconds
Passed Tests: 22
Failed Tests: 0
Skipped Tests: 0
Broken Tests: 0
Warnings: 0
Kernel Version: Linux 5.14.21-150400.24.33-default #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Fri Nov 4 13:55:06 UTC 2022 (76cfe60)
CPU: x86_64
Machine Architecture: x86_64
RAM: 15569564 kB
Swap memory: 2095424 kB
Distro: opensuse-leap
Distro Version: 15.4
Disconnecting from SUT: host
Some basic commands are the following:
# run syscalls and dio testing suites on host
./runltp-ng --run-suite syscalls dio
# run syscalls and dio testing suites in qemu VM
./runltp-ng --sut qemu:image=folder/image.qcow2 \
--run-suite syscalls dio
# run syscalls and dio testing suites via SSH
# NOTE: paramiko and scp packages must be installed in the system
./runltp-ng --sut=ssh:host myhost.com:user=root:key_file=myhost_id_rsa \
--run-suite syscalls dio
It's possible to run a single command before running testing suites using
--run-cmd option as following:
runltp-ng --run-cmd /mnt/testcases/kernel/systemcalls/bpf/bpf_prog02 \
--sut qemu:image=folder/image.qcow2:virtfs=/home/user/ltp \
--ltp-dir /mnt \
--run-suite syscalls dio
It can be used also to run a single command without running testing suites:
runltp-ng --run-cmd /mnt/testcases/kernel/systemcalls/bpf/bpf_prog02 \
--sut qemu:image=folder/image.qcow2
Every session has a temporary directory which can be found in
/<TMPDIR>/runltp-of<username>. Inside this folder there's a symlink
called latest, pointing to the latest session's temporary directory, and the
application will rotate over 5 sessions.
For more information, checkout the following video at the SUSE Labs Conference 2022:
To enable console on a tty device for a VM do:
- open
/etc/default/grub - add
console=$tty_name, console=tty0toGRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX - run
grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
Where $tty_name should be ttyS0, unless virtio serial type is used (i.e.
if you set the serial=virtio backend option, then use hvc0)
Sometimes we need to cover complex testing scenarios, where the SUT uses particular protocols and infrastructures, in order to communicate with our host machine and to execute tests binaries.
For this reason, runltp-ng provides a plugin system to recognize custom SUT
class implementations inside the ltp package folder. Please check host.py
or ssh.py implementations for more details.
Once a new SUT class is implemented and placed inside the ltp package folder,
runltp-ng -s help command can be used to see if application correctly
recognise it.
The application is validated using pytest and pylint.
To run unittests:
pytest
To run linting checks:
pylint --rcfile=pylint.ini ./ltp
The LTP runltp code is hard to read, maintain and some of its parts
are legacy features which are not supported anymore. But if we focus closer on
the results, runltp has done its job for a while since 2001. Nowadays, with
new automation systems, easily accesible virtualization and bigger computing
power, runltp became more and more obsolete, since its main goal was to test
Linux Kernel on target and specific distro(s). Let's take a look at the issues
we have:
- it's hard to maintain and it's based on a mixture of bash/C, both hard to read and not maintained anymore
- it contains many features which are not used and they can be deprecated
- report files are custom format logs or HTML files which are both hard to parse inside i.e. an automation system
- if a test causes system crash, which is common for kernel tests, the tool crashes and we loose most or even all results we obtained before its execution. This means we need to run it inside a virtualized system to be sure that if system crashes, we won't loose control of the machine. And, in any case, we will loose testing report
The last point is really important, since in a world where cloud and embedded
systems are having a big market, we need to provide a usable and a stable way to
test Linux Kernel. Something that runltp is not able to achieve nowadays.
Cyril Hrubis started the first Perl prototype of runltp-ng
(https://github.com/metan-ucw/runltp-ng/), a next generation tests runner that
allows to run tests on a host, as well as inside a Qemu instance or over a SSH.
The tool provided results in a machine parsable format which were easy to
consume by automation systems.
However as the community didn't like the choice of Perl programming language we
decided to switch from Perl to Python to take advantage of the Python community
size, easier maintenance and packages (https://github.com/acerv/runltp-ng).
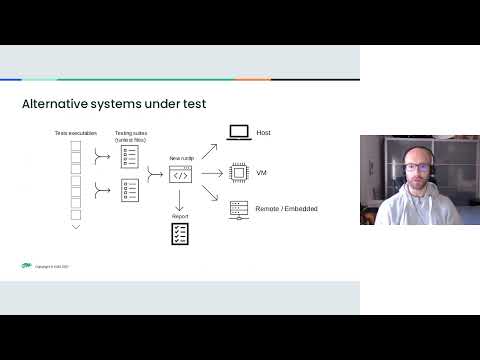
In particular, we tried to focus on missing features and got rid of the ones which were not strictly needed. We ended up with a simple and light tool having the following features:
- test suites can run inside a virtualized system using Qemu or they can be executed via SSH protocol
- runner became more robust so it can gracefully handle kernel crashes and tained statuses of the kernel. At the moment, only Qemu supports this feature
- report file type is JSON by default, so it will be easier to parse with external tools and automation systems
- the user interface has been simplified, so we have two modes: quiet and
verbose mode. The quiet mode is the default one and it shows only tests names
and their results on a list. Verbose mode is similar to the current
runltpstdout
Nowadays runltp-ng is a simple and lightweight implementation that is based on
Python 3.6+ and it doesn't have any dependency from external packages.
Its skeleton is easy to understand and features can be added easily.
A missing feature that is currently under development is the possibility to execute tests via LTX (experimental).
LTX is a small service that runs on target and it permits to communicate via msgpack (https://msgpack.org/) in order to execute binaries on host in the fastest way as possible. Its development is currently maintained by Richard Palethorpe and we plan to make it the default LTP runner in the next future. When LTP metadata file will be completed, LTX will also permit to execute tests in parallel.
By taking in consideration previous topics, we can still provide an usable and
simple tool that can replace current runltp script inside the LTP upstream.
Its usage is simple, pretty stable and we are starting to move forward into
a modern approach to schedule and run tests in the Linux Testing Project.