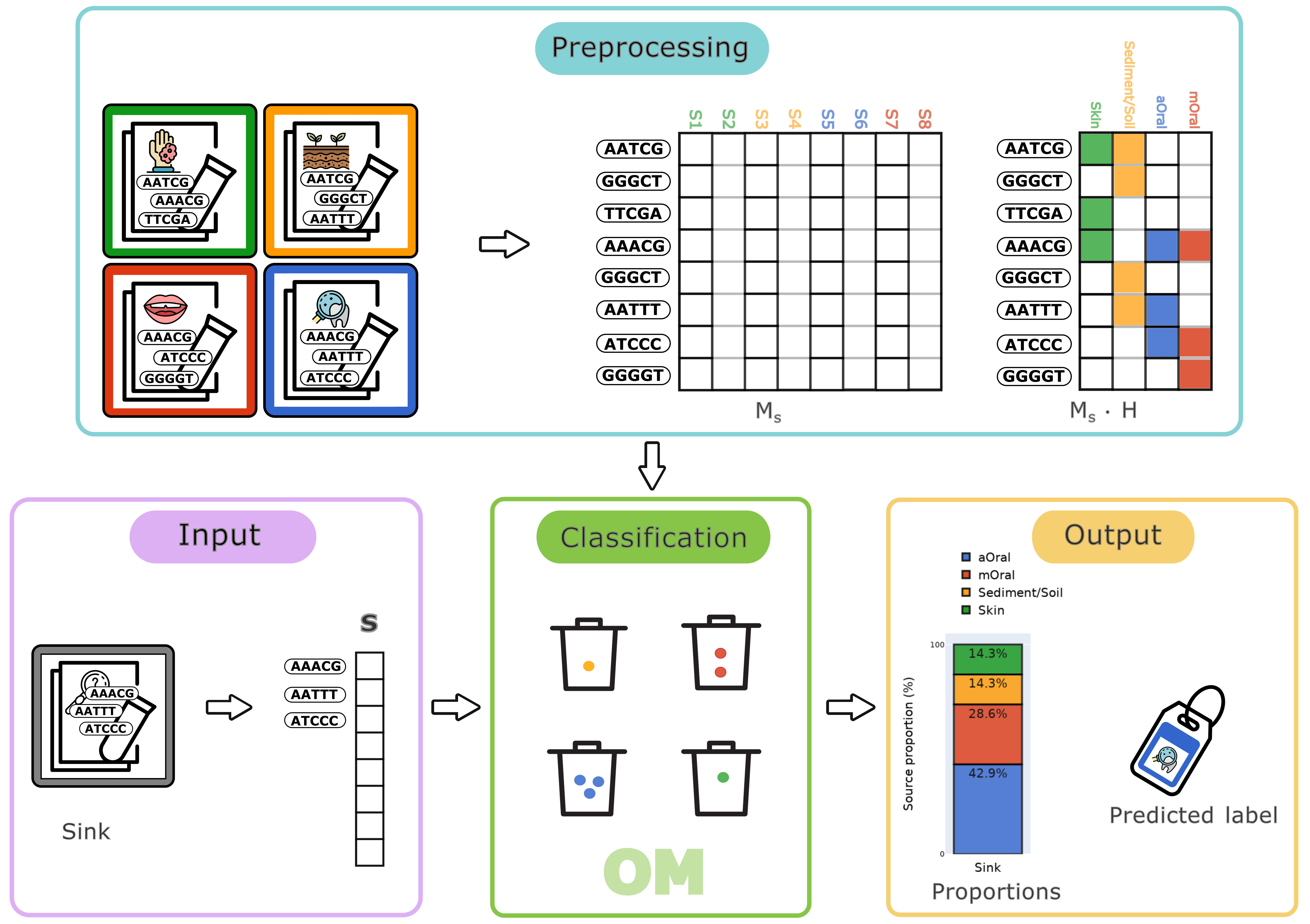
decOM is a high-accuracy microbial source tracking method that is suitable for contamination quantification in paleogenomics, namely the analysis of collections of possibly contaminated ancient oral metagenomic data sets. In few words, if you want to know how contaminated your ancient oral metagenomic sample is, this tool will help 🧹🦷🧹
In longer words decOM comes with a k-mer matrix of ancient Oral(aOral) metagenomic samples and its possible contaminants: Sediment/Soil, Skin and modern oral (mOral). It represents every sink the user inputs as a presence/absence vector of k-mers and then estimates and outputs the proportions of each source environment in the sink. Ex: K-mer AAACG is present in the input sink S and in source S1 labelled as Skin, S5 labelled as aOral and S7 labelled as mOral, hence one ball is added to the bin of Skin, aOral and mOral respectively. After every entry in the the sink vector is compared against every entry of every vector in the sources, decOM outputs the estimated environment proportions and the hard label assigned to the sink
- System requirements
- Installation
- Before running decOM
- Test
- Output files
- Usage
- Additional features
- Command-line options
decOM has been developed and tested under a Linux environment and it only works in Linux-like systems.
It requires certain packages/tools in order to be installed/used:
Install decOM through conda:
git clone https://github.com/CamilaDuitama/decOM.git
cd decOM
conda env create -n decOM --file environment.yml
conda deactivate
conda activate decOM
To make the decOM command available, it is advised to include the absolute path of decOM in your PATH environment variable by adding the following line to your ~/.bashrc file:
export PATH=/absolute/path/to/decOM:${PATH}
Please make sure you read the
decOM you must first download the folder decOM_sources.tar.gz and decompress it. You can either follow the link or use wget (it has to be installed in your computer first):
wget https://zenodo.org/record/6513520/files/decOM_sources.tar.gz
tar -xf decOM_sources.tar.gz
The path of the extracted directory decOM_sources will be requested through the input parameter -p_sources each time decOM is run (see examples below).
You can test if decOM is working by using the aOral sample present in the test/sample/ folder, ex: SRR13355807.
decOM -s SRR13355807 -p_sources decOM_sources/ -k tests/sample/SRR13355807.fof -mem 10GB -t 5
decOM will be your input in -mem times the number of cores (-t). In the previous run we used 10GB * 5 = 50 GB. It is recommended to run regular decOM with at least 10GB of memory and 1 core. If you are testing your own k-mer matrix of sources, please try to allocate at least as much memory as the size (in GB) of your matrix.
You can test if decOM with several sinks by using the files inside test/several_samples/ as follows:
decOM -p_sources decOM_sources/ -p_sinks tests/several_samples/sinks.txt -p_keys tests/several_samples/ -mem 10GB -t 5
decOM relies on DASK for parallelization. Once you start running decOM and the client is set, you can see the diagnostic dashboard to follow the process and better tune parameters such as -mem and -t, make sure you can connect to your local host and visualise it here: http://127.0.0.1:8787/status
decOM will output one .csv file with the k-mer counts and proportions, a folder with the vector representing the sample of interest, from now on called sink (s), and a barplot if indicated by the user.
decOM_output/
├──decOM_output.csv
├──result_plot_sinks.pdf
├──result_plot_sinks.html
├──{s}_vector/
The decOM_output.csv file is a dataframe that contains one row per sink. The columns correspond to the raw number of k-mers per source environment,
the running time per sink, the sink name and the proportions. The result for the one sample explained before should look like this:
| Sediment/Soil | Skin | aOral | mOral | Unknown | Running time (s) | Sink | p_Sediment/Soil | p_Skin | p_aOral | p_mOral | p_Unknown | decOM_max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 182 | 281 | 197859 | 37023 | 334 | 196.7268 | SRR13355807 | 0.0772 | 0.1192 | 83.9527 | 15.7091 | 0.1417 | aOral |
The result_plot_sinks.pdf and result_plot_sinks.html are static and interactive plots (respectively) for the proportions of source environments per sink.
The {s}_vector/ folder is the output of kmtricks filter + kmtricks aggregate.
UNKOWNS IS A FEATURE IN DEVELOPMENT!: The contribution of an unknown source is a feature in development. For a more accurate assessment of the contamination proportions in a sample, please take into account the raw counts for Sediment/Soil, Skin, aOral, mOral.
You can use as input your fastq/fasta file from your own experiment, you can download an ancient oral sample of interest from the AncientMetagenomeDir or from the SRA.
The users of decOM can represent their own metagenomic sample as a presence/absence vector of k-mers using kmtricks. This sink can be compared against the collection of sources we have put together.
Once you have downloaded the folder with the matrix of sources and the fastq file(s) of your sink(s), you have to create a key.fof file per sink.
The key.fof has one line of text depending on your type of data:
-Single-end:
s : path/to/file/s_1.fastq.gz
-Paired-end :
s : path/to/file/s_1.fastq.gz; path/to/file/s_2.fastq.gz
decOM relies on kmtricks, you might use a FASTA or FASTQ format, gzipped or not, which means you have to change the key.fof file accordingly.
Since you now have the fasta/fastq file of your sink, the folder with the matrix of sources and the key file, simply run decOM as follows:
decOM -s {SINK} -p_sources decOM_sources/ -k {KEY.FOF} -mem {MEMORY} -t {THREADS}
The parameter -s refers to the name of the sink, whereas the parameter -k is the path to the file key.fof. Make sure that the name you use for your sink is the same as the name you use in the key.fof. So if your sink is called s, -s s_1, your key.fof should be s_1 : s_1.fastq
If you want to assess the contamination of several sinks, you need one key.fof file per sink, and they must be inside the folder p_sources
decOM -p_sinks {PATH_SINKS} -p_sources decOM_sources/ -p_keys {PATH_KEYS} -mem {MEMORY} -t {THREADS}
The parameter -p_sinks refers to a .txt file with a list of sinks limited by a newline (\n). Each sink in this file must have a corresponding key.fof file in the folder p_keys/ . While p_sinks is the path to a file, p_keys is a path to a folder that should contain as many key.fof files as sinks.
If you have n samples, your the content of the file p_sinks should be:
s_1
s_2
s_3
.
.
.
s_n
And the content of p_keys should be:
p_keys/
├──s_1.fof
├──s_2.fof
├──s_3.fof
.
.
.
├──s_n.fof
This feature was thought for the users who prefered having mOral, Skin and Sediment/Soil samples as sources but no aOral samples. Once you download and unzip the new matrix of sources:
wget https://zenodo.org/record/6772124/files/aOralOut_sources.tar.gz
tar -xf aOralOut_sources.tar.gz
Simply run decOM-aOralOut as follows:
decOM-aOralOut -s SRR13355807 -p_sources aOralOut_sources/ -k tests/sample/SRR13355807.fof -mem 10GB -t 5
This feature was thought for the users who prefer building their own k-mer matrix of sources. To run decOM-MST you need to create your own p_sources folder and additionally you need a -m or map file with one label per source.
To create the p_sources you can run kmtricks (already in your conda environment for decOM) as follows:
kmtricks pipeline --file kmtricks.fof --run-dir p_sources --mode kmer:pa:bin --restrict-to-list 1
kmtricks aggregate --run-dir p_sources --pa-matrix kmer --output p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa --format bin
kmtricks dump --run-dir p_sources --input p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa.lz4 -o p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa.txt
kmtricks will tell you how many partitions are expected in total. Ex: --restrict-to-list 1,2,3
You additionally need a -m file which is a .csv file of two columns: Env and SampleID. This is a x by 2 table, where x is the number of sources in your input k-mer matrix (number of columns in the kmtricks.fof used to run kmtricks). SampleID refers to the unique identifier of each source sample, and Env is the corresponding label for the source environment from where each sample was taken.
You can run decOM-MST with test data as follows:
kmtricks pipeline --file tests/MST/kmtricks.fof --run-dir p_sources --mode kmer:pa:bin --restrict-to-list 1
kmtricks aggregate --run-dir p_sources --pa-matrix kmer --output p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa --format bin
kmtricks dump --run-dir p_sources/ --input p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa -o p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa.txt
decOM-MST -s SRR13355807 -p_sources p_sources/ -m tests/MST/map.csv -k tests/sample/SRR13355807.fof --mem 10GB -t 5
This feature was thought for the users who would like to perform a leave-one-out experiment on their own matrix of sources. This experiment consist on creating a k-mer matrix of sources, extracting one sample to be used as sink and leave the reas out as sources. Once this iteration is finished, decOM-LOO would take out a different sink from the matrix of sources, and compare it against the rest of samples.decOM-LOO stops once every sample has been compared against the rest. To run decOM-LOO you need to create your own p_sources folder and additionally you need a -m or map file with one label per source.
To create the p_sources you can run kmtricks (already in your conda environment for decOM) as follows:
kmtricks pipeline --file kmtricks.fof --run-dir p_sources --mode kmer:pa:bin
kmtricks aggregate --run-dir p_sources --pa-matrix kmer --output p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa --format bin
kmtricks dump --run-dir p_sources --input p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa.lz4 -o p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa.txt
decOM-LOO has not been tested.
You additionally need a -m file which is a .csv file of two columns: Env and SampleID. This is a x by 2 table, where x is the number of sources in your input k-mer matrix (number of columns in the kmtricks.fof used to run kmtricks). SampleID refers to the unique identifier of each source sample, and Env is the corresponding label for the source environment from where each sample was taken.
You can run decOM-LOO with test data as follows:
kmtricks pipeline --file tests/LOO/kmtricks.fof --run-dir p_sources --mode kmer:pa:bin
kmtricks aggregate --run-dir p_sources --pa-matrix kmer --output p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa --format bin
kmtricks dump --run-dir p_sources/ --input p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa -o p_sources/matrices/matrix.pa.txt
decOM-LOO -p_sources p_sources/ -m tests/LOO/map.csv --mem 10GB -t 5
usage: decOM [-h] (-s SINK | -p_sinks PATH_SINKS) -p_sources PATH_SOURCES (-k KEY | -p_keys PATH_KEYS) -mem MEMORY -t THREADS [-o OUTPUT] [-p {True,False}] [-V] [-v]
Microbial source tracking for contamination assessment of ancient oral samples using k-mer-based methods
Argurguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-s SINK, --sink SINK Write down the name of your sink. It must be the same as the first element of key.fof. When this argument is set, -k/--key must be defined too
-p_sinks PATH_SINKS, --path_sinks PATH_SINKS
.txt file with a list of sinks limited by a newline (\n). When this argument is set, -p_keys/--path_keys must be defined too.
-p_sources PATH_SOURCES, --path_sources PATH_SOURCES
path to folder downloaded from https://zenodo.org/record/6513520/files/decOM_sources.tar.gz
-k KEY, --key KEY filtering key (a kmtricks fof with only one sample). When this argument is set, -s/--sink must be defined too.
-p_keys PATH_KEYS, --path_keys PATH_KEYS
Path to folder with filtering keys (a kmtricks fof with only one sample).You should have as many .fof files as sinks.When this argument is set,
-p_sinks/--path_sinks must be defined too.
-mem MEMORY, --memory MEMORY
Write down how much memory you want to use for this process. Ex: 10GB
-t THREADS, --threads THREADS
Number of threads to use. Ex: 5
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
Path to output folder, where you want decOM to write the results. Folder must not exist, it won't be overwritten.
-p {True,False}, --plot {True,False}
True if you want a plot (in pdf and html format) with the source proportions of the sink, else False
-V, --version Show version number and exit
-v, --verbose Verbose output