Package implements a number local outlier factor algorithms for outlier detection and finding anomalous data
- LOF
- LDOF (Local Density Outlier Factor)
- LOCI (Local outlier correlation integral)
- CBLOF (Cluster-based LOF)
Add the following dependency to your POM file:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.chen0040</groupId>
<artifactId>java-local-outlier-factor</artifactId>
<version>1.0.4</version>
</dependency>The anomaly detection algorithms takes data that is prepared and stored in a data frame (Please refers to this link on how to create a data frame from file or from scratch)
All LOF algorithms variants use unsupervised-learning for training.
The following method trains an algorithm:
lof.fitAndTransform(dataFrame);The following method returns true if the dataRow (which is a row in a data frame) taken in is an outlier:
boolean isOutlier = lof.isAnomaly(dataRow);To create and train the LOF, run the following code:
LOF method = new LOF();
method.setMinPtsLB(3);
method.setMinPtsUB(15);
method.setThreshold(0.2);
DataFrame resultantTrainedData = method.fitAndTransform(trainingData);
System.out.println(resultantTrainedData.head(10));To test the trained method on new data, run:
boolean outlier = method.isAnomaly(dataRow);The create and train the LOF, run the following code:
CBLOF method = new CBLOF();
DataFrame resultantTrainedData = method.fitAndTransform(trainingData);
System.out.println(resultantTrainedData.head(10));To test the trained method on new data, run:
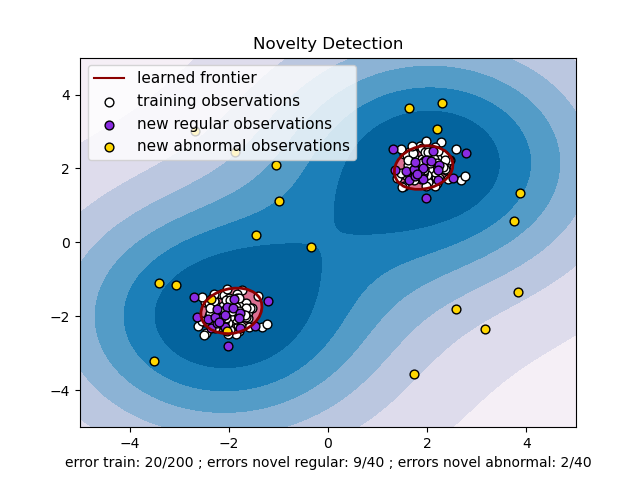
boolean outlier = method.isAnomaly(dataRow);The problem that we will be using as demo as the following anomaly detection problem:
Below is the sample code which illustrates how to use LOF to detect outliers in the above problem:
DataQuery.DataFrameQueryBuilder schema = DataQuery.blank()
.newInput("c1")
.newInput("c2")
.newOutput("anomaly")
.end();
Sampler.DataSampleBuilder negativeSampler = new Sampler()
.forColumn("c1").generate((name, index) -> randn() * 0.3 + (index % 2 == 0 ? -2 : 2))
.forColumn("c2").generate((name, index) -> randn() * 0.3 + (index % 2 == 0 ? -2 : 2))
.forColumn("anomaly").generate((name, index) -> 0.0)
.end();
Sampler.DataSampleBuilder positiveSampler = new Sampler()
.forColumn("c1").generate((name, index) -> rand(-4, 4))
.forColumn("c2").generate((name, index) -> rand(-4, 4))
.forColumn("anomaly").generate((name, index) -> 1.0)
.end();
DataFrame data = schema.build();
data = negativeSampler.sample(data, 20);
data = positiveSampler.sample(data, 20);
System.out.println(data.head(10));
LOF method = new LOF();
method.setParallel(true);
method.setMinPtsLB(3);
method.setMinPtsUB(10);
method.setThreshold(0.5);
DataFrame learnedData = method.fitAndTransform(data);
BinaryClassifierEvaluator evaluator = new BinaryClassifierEvaluator();
for(int i = 0; i < learnedData.rowCount(); ++i){
boolean predicted = learnedData.row(i).categoricalTarget().equals("1");
boolean actual = data.row(i).target() == 1.0;
evaluator.evaluate(actual, predicted);
logger.info("predicted: {}\texpected: {}", predicted, actual);
}Below is the sample code which illustrates how to use CBLOF to detect outliers in the above problem:
DataQuery.DataFrameQueryBuilder schema = DataQuery.blank()
.newInput("c1")
.newInput("c2")
.newOutput("anomaly")
.end();
Sampler.DataSampleBuilder negativeSampler = new Sampler()
.forColumn("c1").generate((name, index) -> randn() * 0.3 + (index % 2 == 0 ? -2 : 2))
.forColumn("c2").generate((name, index) -> randn() * 0.3 + (index % 2 == 0 ? -2 : 2))
.forColumn("anomaly").generate((name, index) -> 0.0)
.end();
Sampler.DataSampleBuilder positiveSampler = new Sampler()
.forColumn("c1").generate((name, index) -> rand(-4, 4))
.forColumn("c2").generate((name, index) -> rand(-4, 4))
.forColumn("anomaly").generate((name, index) -> 1.0)
.end();
DataFrame data = schema.build();
data = negativeSampler.sample(data, 200);
data = positiveSampler.sample(data, 200);
System.out.println(data.head(10));
CBLOF method = new CBLOF();
method.setParallel(false);
DataFrame learnedData = method.fitAndTransform(data);
BinaryClassifierEvaluator evaluator = new BinaryClassifierEvaluator();
for(int i = 0; i < learnedData.rowCount(); ++i){
boolean predicted = learnedData.row(i).categoricalTarget().equals("1");
boolean actual = data.row(i).target() == 1.0;
evaluator.evaluate(actual, predicted);
logger.info("predicted: {}\texpected: {}", predicted, actual);
}
evaluator.report();Below is the sample code which illustrates how to use LDOF to detect outliers in the above problem:
DataQuery.DataFrameQueryBuilder schema = DataQuery.blank()
.newInput("c1")
.newInput("c2")
.newOutput("anomaly")
.end();
Sampler.DataSampleBuilder negativeSampler = new Sampler()
.forColumn("c1").generate((name, index) -> randn() * 0.3 + (index % 2 == 0 ? -2 : 2))
.forColumn("c2").generate((name, index) -> randn() * 0.3 + (index % 2 == 0 ? -2 : 2))
.forColumn("anomaly").generate((name, index) -> 0.0)
.end();
Sampler.DataSampleBuilder positiveSampler = new Sampler()
.forColumn("c1").generate((name, index) -> rand(-4, 4))
.forColumn("c2").generate((name, index) -> rand(-4, 4))
.forColumn("anomaly").generate((name, index) -> 1.0)
.end();
DataFrame data = schema.build();
data = negativeSampler.sample(data, 20);
data = positiveSampler.sample(data, 20);
System.out.println(data.head(10));
LDOF method = new LDOF();
DataFrame learnedData = method.fitAndTransform(data);
BinaryClassifierEvaluator evaluator = new BinaryClassifierEvaluator();
for(int i = 0; i < learnedData.rowCount(); ++i) {
boolean predicted = learnedData.row(i).categoricalTarget().equals("1");
boolean actual = data.row(i).target() == 1.0;
evaluator.evaluate(actual, predicted);
logger.info("predicted: {}\texpected: {}", predicted, actual);
}
evaluator.report();Below is the sample code which illustrates how to use LOCI to detect outliers in the above problem:
DataQuery.DataFrameQueryBuilder schema = DataQuery.blank()
.newInput("c1")
.newInput("c2")
.newOutput("anomaly")
.end();
Sampler.DataSampleBuilder negativeSampler = new Sampler()
.forColumn("c1").generate((name, index) -> randn() * 0.3 + (index % 2 == 0 ? -2 : 2))
.forColumn("c2").generate((name, index) -> randn() * 0.3 + (index % 2 == 0 ? -2 : 2))
.forColumn("anomaly").generate((name, index) -> 0.0)
.end();
Sampler.DataSampleBuilder positiveSampler = new Sampler()
.forColumn("c1").generate((name, index) -> rand(-4, 4))
.forColumn("c2").generate((name, index) -> rand(-4, 4))
.forColumn("anomaly").generate((name, index) -> 1.0)
.end();
DataFrame data = schema.build();
data = negativeSampler.sample(data, 20);
data = positiveSampler.sample(data, 20);
System.out.println(data.head(10));
LOCI method = new LOCI();
method.setAlpha(0.5);
method.setKSigma(3);
DataFrame learnedData = method.fitAndTransform(data);
BinaryClassifierEvaluator evaluator = new BinaryClassifierEvaluator();
for(int i = 0; i < learnedData.rowCount(); ++i){
boolean predicted = learnedData.row(i).categoricalTarget().equals("1");
boolean actual = data.row(i).target() == 1.0;
evaluator.evaluate(actual, predicted);
logger.info("predicted: {}\texpected: {}", predicted, actual);
}