Library for non-linear geometry computations in Java.
The library was developed with the following objectives in mind
- trajectory design for autonomous robots
- suitable for use in safety-critical real-time systems
- implementation of theoretical concepts with high level of abstraction
- biinvariant distance vectors
- biinvariant barycentric coordinates, iterative coordinates
- biinvariant mean, spatial median
- filtering (using geodesic averages, biinvariant mean)
- parallel transport: pole ladder, schild's ladder
- kriging
- Bézier-, spline-, radial basis function interpolation
- curve subdivision, Hermite curve subdivision
- clothoid
- Dubins path
- barycentric coordinates for polygons: mean value, discrete harmonic, ...
- Ramer-Douglas-Peucker algorithm for curve decimation
- Graham scan for convex hull in the plane
- rigid motion fit, sphere fit
- Baker Campbell Hausdorff formula
- Clifford algebra, geometric product
- n-dimensional sphere
$S^n$ - n-dimensional hyperbolic space
$H^n$ - Grassmann manifold
Gr(n,k) - n-dimensional projective space
RP^n - symmetric positive definite matrices
SPD(n) - Stiefel manifold
St(n,k)
- Euclidean space
$R^n$ - Heisenberg group
He(n) - Special orthogonal group
SO(n) - Special Euclidean groups
SE(2),SE(2)covering,SE(3)
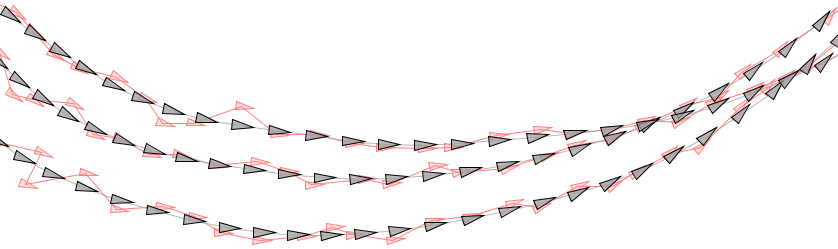
Abstract: We demonstrate that curve subdivision in the special Euclidean group SE(2) allows the design of planar curves with favorable curvature. We state the non-linear formula to position a point along a geodesic in SE(2). Curve subdivision in the Lie group consists of trigonometric functions. When projected to the plane, the refinement method reproduces circles and straight lines. The limit curves are designed by intuitive placement of control points in SE(2).
Figure: A point in the special Euclidean group SE(2) consists of a position in the plane and a heading. The figure shows two rounds of cubic B-spline subdivision of an initial sequence of five control points in SE(2). A point is indicated by an arrowhead.
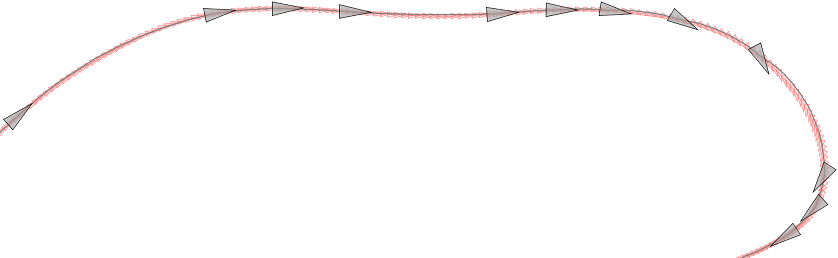
Abstract: Geodesic averages have been used to generalize curve subdivision and Bézier curves to Riemannian manifolds and Lie groups. We show that geodesic averages are suitable to perform smoothing of sequences of data in nonlinear spaces. In applications that produce temporal uniformly sampled manifold data, the smoothing removes high-frequency components from the signal. As a consequence, discrete differences computed from the smoothed sequence are more regular. Our method is therefore a simpler alternative to the extended Kalman filter. We apply the smoothing technique to noisy localization estimates of mobile robots.
Figure: A sequence of noisy localization estimates of a fast driving go-kart in red, and the result of smoothing in black.
Abstract: We present meshfree generalized barycentric coordinates for scattered sets of points in d-dimensional vector space. The coordinates satisfy the Lagrange property. Our derivation is based on the projection of Shepard's popular inverse distance weights to their best fit in the subspace of coordinates with linear reproduction. The notion of distance between a pair of points is sufficient for the construction of coordinates.
Figure: Basis functions of inverse distance weighting, affine coordinates, and inverse distance coordinates for an example set of six points in the plane.
Abstract: We construct biinvariant generalized barycentric coordinates for scattered sets of points in any Lie group. The coordinates are invariant under left-action, right-action, and inversion, and satisfy the Lagrange property. The construction does not utilize a metric on the Lie group, unlike inverse distance coordinates. Instead, proximity is determined in a vector space of higher dimensions than the group using the Euclidean norm. The coordinates that we propose are an inverse to the unique, biinvariant weighted average in the Lie group.
Figure: Basis functions of inverse distance weighting, inverse distance coordinates, and biinvariant coordinates with exponent β=2 for an example set of six points in the unit square.
Abstract: We construct biinvariant vector valued functions of relative distances using the influence matrix, and the Mahalanobis distance defined by scattered sets of points on Lie groups. The functions are invariant under all group operations. Distance vectors define an ordering of the points in the scattered set with respect to a group element. Applications are classification, inverse distance weighting, and the construction of generalized barycentric coordinates for the purpose of deformation, and domain transfer.
Figure: Applications of biinvariant distance vectors and weightings: a) classification task in the Lie group SE(2),
b) kriging function
B-Spline curves in SE(2) produced by DeBoor Algorithm or curve subdivision produce curves in the planar subspace
The sequence of localization estimates of a mobile robot often contains noise.
Instead of using a complicated extended Kalman filter, geodesic averages based on conventional window functions denoise the uniformly sampled signal of poses in SE(2).
The pose of mobile robots is typically recorded at high frequencies. The trajectory can be faithfully reconstructed from a fraction of the samples.
Jan Hakenberg, Oliver Brinkmann, Joel Gächter
From time to time, a version is deployed and made available for maven integration. Specify repository and dependency of the library sophus in the pom.xml file of your maven project:
<dependencies>
<!-- other dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.alpine</groupId>
<artifactId>sophus</artifactId>
<version>0.0.9</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<repositories>
<!-- other repositories -->
<repository>
<id>sophus-mvn-repo</id>
<url>https://raw.github.com/datahaki/sophus/mvn-repo/</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>The source code is attached to every release.
The branch master always contains the latest features for Java 17, and does not correspond to the most recent deployed version generally.
- Bi-invariant Means in Lie Groups. Application to Left-invariant Polyaffine Transformations. by Vincent Arsigny, Xavier Pennec, Nicholas Ayache
- Exponential Barycenters of the Canonical Cartan Connection and Invariant Means on Lie Groups by Xavier Pennec, Vincent Arsigny
- Lie Groups for 2D and 3D Transformations by Ethan Eade
- Manifold-valued subdivision schemes based on geodesic inductive averaging by Nira Dyn, Nir Sharon
- Power Coordinates: A Geometric Construction of Barycentric Coordinates on Convex Polytopes by Max Budninskiy, Beibei Liu, Yiying Tong, Mathieu Desbrun
- Generalized Barycentric Coordinates in Computer Graphics and Computational Mechanics by Kai Hormann, N. Sukumar
- Barycentric Subspace Analysis on Manifolds by Xavier Pennec
- Least-Squares Rigid Motion Using SVD by Olga Sorkine-Hornung, Michael Rabinovich
- Clothoid Fitting and Geometric Hermite Subdivision by Ulrich Reif, Andreas Weinmann arxiv
- Iterative coordinates by Chongyang Deng, Qingjun Chang, Kai Hormann