This is a simple library to implement Binary decision Trees.
In computer science, a binary decision diagram (BDD) or branching program is a data structure that is used to represent a Boolean function. On a more abstract level, BDDs can be considered as a compressed representation of sets or relations. Unlike other compressed representations, operations are performed directly on the compressed representation, i.e. without decompression.
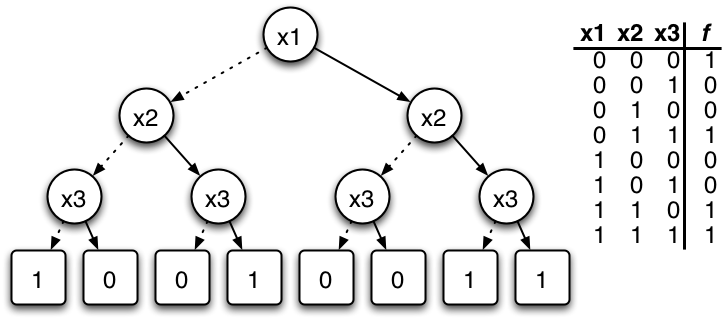
A simple example of this would be the following tree:
Each node has a pair of childs, one child is the one associated to its father when the function inside the father returns a true value, and the other is associated when the fathers function returns false.
You can create the nodes manually as python objects like is shown in this example:
from bdt.tree import BDT
from bdt.node import Node
true_node = Node(
'True Node'
)
false_node = Node(
'False Node'
)
head_node = Node(
'Head Node',
lambda var: var < 10,
true_child=true_node,
false_child=false_node
)
tree = BDT(
head_node
)Other option is to create the tree by passing a python dictionary:
from bdt.tools import tree_from_dict
tree_dict = {
'head': 'Head Node',
'variables': [
'withd',
'height'
],
'nodes': [
{
'name': 'Head Node',
'function': 'withd * height < 50',
'true_child': 'True Node',
'false_child': 'False Node'
},
{
'name': 'True Node',
'function': 'withd * height < 25',
'true_child': 'True True Node',
'false_child': 'True False Node'
},
{
'name': 'False Node',
'function': 'withd * height < 100',
'true_child': 'False True Node',
'false_child': 'False False Node'
},
{
'name': 'True True Node',
'function': 'None',
'true_child': 'None',
'false_child': 'None'
},
{
'name': 'True False Node',
'function': 'None',
'true_child': 'None',
'false_child': 'None',
},
{
'name': 'False True Node',
'function': 'None',
'true_child': 'None',
'false_child': 'None'
},
{
'name': 'False False Node',
'function': 'None',
'true_child': 'None',
'false_child': 'None'
},
]
}
tree = tree_from_dict(tree_dict)And the final form would be to load it from a JSON file the matches the previous dictionary and load it by using:
import json
from bdt.tools import tree_from_json
json_data = open('{PATH_TO_FILE/file.json}', 'r')
tree = tree_from_json(json_data)And the final form would be to load it from a JSON file the matches the previous dictionary and load it by using:
import json
from bdt.tools import tree_from_json
json_data = open('{PATH_TO_FILE/file.json}', 'r')
tree = tree_from_json(json_data)To traverse the created tree yo can makeit like this:
import json
from bdt.tools import tree_from_json
json_data = open('{PATH_TO_FILE/file.json}', 'r')
tree = tree_from_json(json_data)
tree.set_parameters({
'withd': 25,
'height': 25
})
for node in tree:
print node.nameThe set_parameters function let you initialize the values needed to run the boolean functions inside each node.
To use pandas you can use the PandasNode and PandasBDT calsses, this can be used only by the object creation, nor JSON nor DICT creation are allowed for this class.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from bdt.tree import PandasBDT
from bdt.node import PandasNode
true_child = PandasNode(
'True Node'
)
false_child = PandasNode(
'False Node'
)
head = PandasNode(
'Node',
lambda df: df['vals'] > 5,
pd.DataFrame(
np.matrix(
range(10)
).T,
columns=['vals']
),
true_child,
false_child
)
tree = PandasBDT(
head
)To traverse the tree is different from the standard execution, you'll need to run the execute method instead of iterating over the tree, after doing that you can search for the leave nodes and from that get the correspongin frame for each node.
tree.execute()
leaves = tree.get_leaves()
for node in leaves:
print node.data_frame