The MFRC522 class is designed for controlling MFRC522 RFID modules using MicroPython. It provides various methods to interact with RFID cards, authenticate, read, and write data to the cards.
The RC522 RFID Module is a popular RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) reader and writer module widely used for various applications such as access control systems, authentication, and tracking. This module operates at 13.56 MHz and communicates with microcontrollers or single-board computers like the Raspberry Pi.
- RFID Compatibility: The RC522 module supports ISO14443A standard RFID cards, tags, and key fobs.
- SPI Interface: It communicates with the host microcontroller via the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) protocol, making it compatible with a wide range of microcontrollers.
- Secure Communication: The module provides secure authentication and data transmission between the RFID card/tag and the host device.
- Multiple Antennas: It supports multiple antennas for better performance and flexibility in various applications.
- Low Power Consumption: The RC522 module is designed to be power-efficient, suitable for battery-powered projects.
- Open-Source Libraries: Several open-source libraries and software examples are available for interfacing with the module, simplifying development.
Here is the pinout of the RC522 RFID Module:
- VCC: Connect this pin to the power supply voltage (usually 3.3V).
- RST: Reset pin for the module.
- GND: Connect this pin to the ground of the power supply.
- IRQ: Optional interrupt pin, depending on the application.
- MISO: SPI Master In Slave Out.
- MOSI: SPI Master Out Slave In.
- SCK: SPI Clock.
- SDA: SPI Data Input/Output.
The RC522 module communicates with RFID cards and tags using radio-frequency signals. When an RFID card/tag is brought into proximity with the module's antenna, it sends a request, and if the card is valid, data is exchanged securely. The module can read unique identification numbers from RFID cards/tags, allowing you to implement various applications like access control, attendance systems, and more.
To get started with the RC522 RFID Module, you'll need a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi), appropriate libraries, and RFID cards/tags. Connect the module to your microcontroller using the SPI interface and power it up. Then, use the provided libraries and example code to read and write data to RFID cards/tags.
The RC522 module is versatile and finds applications in security systems, inventory management, and interactive projects that require RFID technology.
For detailed usage instructions and code examples, refer to the documentation and resources available for your specific microcontroller platform.
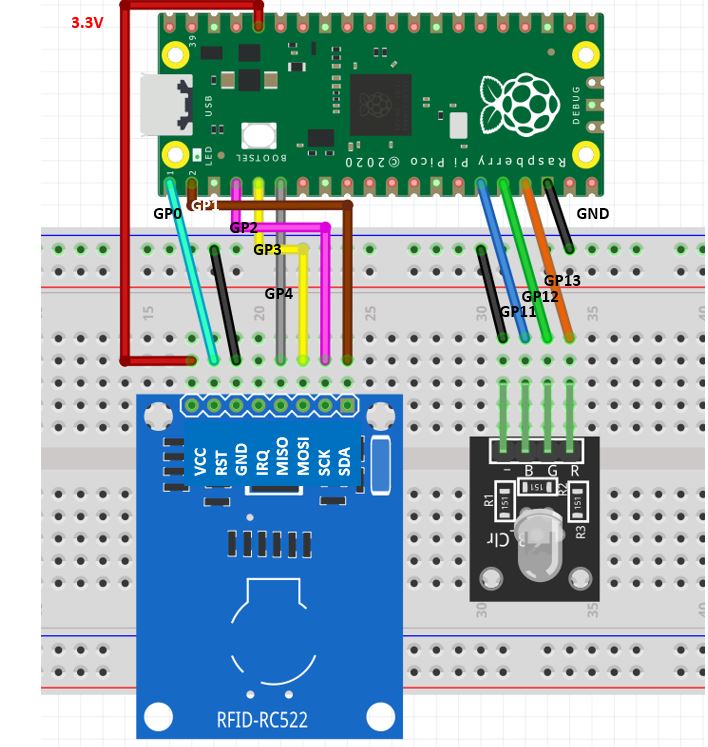
| RC522 RFID Reader Module | Raspberry Pi Pico |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V |
| RST | GP0 |
| GND | GND |
| IRQ | Not connected |
| MISO | GP4 |
| MOSI | GP3 |
| SCK | GP2 |
| SDA | GP1 |
In this table, we present the connection between the Raspberry Pi Pico and the RC522 RFID reader module. The VCC (power supply) and GND (ground) wires of the module should be connected to the 3.3V and GND pins of the Raspberry Pi Pico to ensure proper module operation. The RST (reset) and IRQ (interrupt) wires can be connected or omitted depending on specific functions. The MISO, MOSI, and SCK wires are used for SPI communication and should be connected to the corresponding GPIO pins. The SDA wire is also used in SPI communication.
- Initializes the MFRC522 instance.
- Parameters:
sck: The pin for the SPI clock signal.mosi: The pin for the SPI Master Out Slave In (MOSI) signal.miso: The pin for the SPI Master In Slave Out (MISO) signal.rst: The pin for resetting the MFRC522 module.cs: The pin for the chip select (CS) signal.baudrate: The SPI baud rate (default is 1,000,000).spi_id: The SPI interface ID (default is 0).
- Writes a value to a register.
- Parameters:
reg: The register address.val: The value to write to the register.
- Reads a value from a register.
- Parameters:
reg: The register address.
- Returns:
- The value read from the register.
- Sets specific bits in a register to 1.
- Parameters:
reg: The register address.mask: The bitmask to set.
- Clears specific bits in a register to 0.
- Parameters:
reg: The register address.mask: The bitmask to clear.
- Sends data to the RFID card and receives a response.
- Parameters:
cmd: The command code to send to the card.send: The data to send to the card.
- Returns:
stat: Status code (OK, NOTAGERR, or ERR).recv: Received data from the card.bits: Number of bits received.
- Calculates and returns the CRC value for a given data array.
- Parameters:
data: The data for which to calculate the CRC.
- Returns:
- CRC values as a list [CRC1, CRC2].
- Initializes the MFRC522 module with default settings.
- Resets the MFRC522 module.
- Enables or disables the antenna of the MFRC522 module.
- Parameters:
on: Boolean value to enable or disable the antenna (default is True).
- Sends a request to a nearby RFID card.
- Parameters:
mode: Request mode (REQIDL or REQALL).
- Returns:
stat: Status code (OK or ERR).bits: Number of bits received.
- Performs anti-collision for RFID cards.
- Parameters:
anticolN: Anti-collision number.
- Returns:
stat: Status code (OK or ERR).recv: Received data from the card.
- Selects an RFID card with the given UID.
- Parameters:
uid: The UID of the card.
- Returns:
stat: Status code (OK or ERR).uid: The UID of the selected card.
- Converts a list of values to a hexadecimal string.
- Parameters:
v: List of values to convert.
- Returns:
- A hexadecimal string representation of the values.
- Authenticates with an RFID card.
- Parameters:
mode: Authentication mode (AUTHENT1A or AUTHENT1B).addr: Address to authenticate.sect: Sector data.ser: Card serial number.
- Returns:
- Status code (OK or ERR).
- Authenticates with an RFID card using keys.
- Parameters:
uid: Card UID.addr: Address to authenticate.keyA: Key A (optional).keyB: Key B (optional).
- Returns:
- Status code (OK or ERR).
- Stops cryptographic authentication.
- Reads data from an RFID card.
- Parameters:
addr: Address to read from.
- Returns:
- Status code (OK or ERR).
recv: Received data.
- Writes data to an RFID card.
- Parameters:
addr: Address to write to.data: Data to write.
- Returns:
- Status code (OK or ERR).
- Writes data to a specific block within a sector.
- Parameters:
uid: Card UID.sector: Sector to write to.block: Block within the sector to write to.data: Data to write.keyA: Key A (optional).keyB: Key B (optional).
- Returns:
- Status code (OK or ERR).
- Reads data from a specific block within a sector.
- Parameters:
uid: Card UID.sector: Sector to read from.block: Block within the sector to read from.keyA: Key A (optional).keyB: Key B (optional).
- Returns:
- Status code (OK or ERR).
recv: Received data.
- Dumps data from a Classic 1K RFID card.
- Parameters:
uid: Card UID.Start: Starting block (default is 0).End: Ending block (default is 64).keyA: Key A (optional).keyB: Key B (optional).
- Returns:
- Status code (OK or ERR).