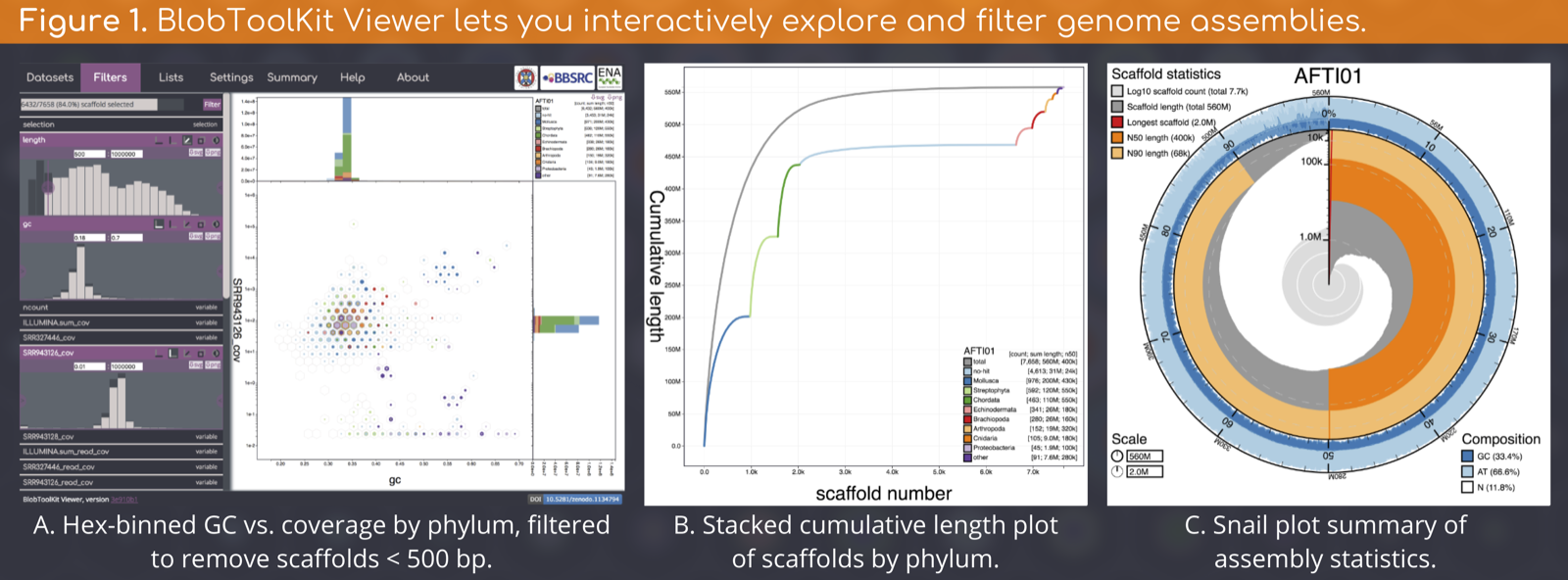
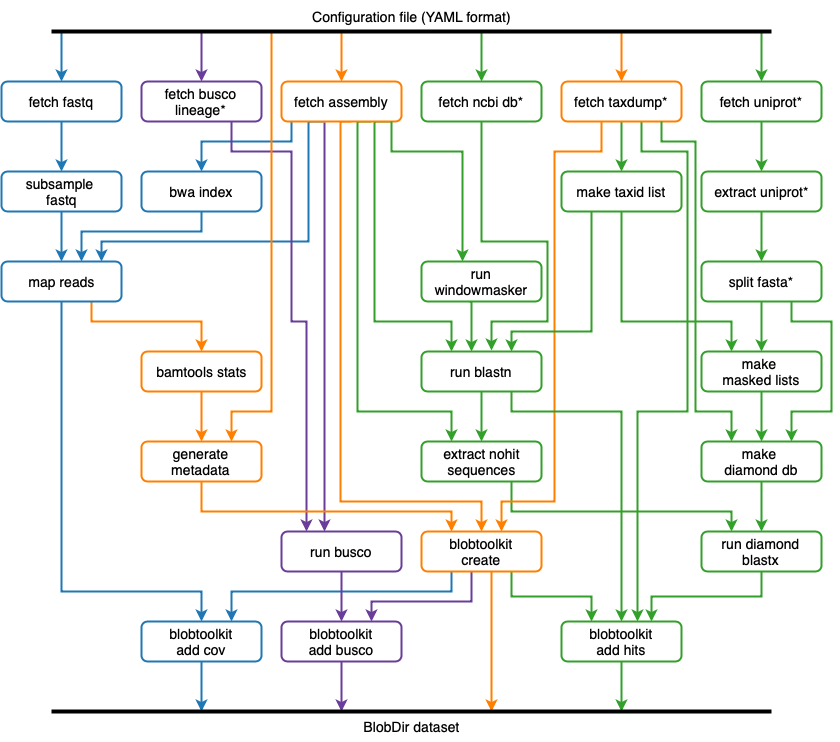
A Snakemake pipeline to run analyses on public genome assemblies for visualisation in the BlobToolKit Viewer
While designed for use on public genome assemblies and read files, this pipeline is also suitable for use with local assembly and read files. If the assembly and read files exist locally in the working directory when the pipeline is run, the remote fetches will be skipped.
More information and tutorials are available at blobtoolkit.genomehubs.org/pipeline/
The final output of this pipeline is a BlobDir dataset directory containing a set of JSON files ready for interactive visualisation with the BlobToolKit Viewer (Figure 1).
The pipeline (Figure 2) is implemented using Snakemake and will fetch all required database and assembly files then run BLAST/Diamond similarity searches and bwa/minimap2 read mapping and for processing with BlobTools.
Most dependencies are handled by Snakemake. To get started you will need to install Conda, BLAST+, BlobTools2 and the BlobToolKit viewer, then use Conda to install Snakemake. The instructions below assume installation on Linux.
See conda.io
$ wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
$ bash Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
If the conda command is not available after installation, it may be necessary to add an entry to your ~/.bashrc file, i.e.:
$ echo ". $HOME/miniconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.sh" >> ~/.bashrc
Some pipeline dependencies are loaded from non-default channels. To add these to your local Conda config, run the following commands:
$ conda config --add channels bioconda
$ conda config --add channels conda-forge
$ conda config --add channels r
Download relevant binary from ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.govblast/executables/blast+. BlobToolKit requires at least version 2.8.
$ wget ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/executables/blast+/2.8.1/ncbi-blast-2.8.1+-x64-linux.tar.gz
$ tar xvf ncbi-blast-2.8.1+-x64-linux.tar.gz
Running the pipeline requires BlobTools2 and visualisation of processed datasets requires the BlobToolKit Viewer. To install both, follow the BlobTools2 installation instruction.
$ conda create -n blobtools2 -y python=3.6 docopt pyyaml ujson tqdm nodejs
$ conda activate blobtools2
$ conda install -c bioconda pysam seqtk
$ mkdir -p taxdump
$ cd taxdump
$ curl -L ftp://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/pub/taxonomy/new_taxdump/new_taxdump.tar.gz | tar xzf -
$ cd ..
$ git clone https://github.com/blobtoolkit/blobtools2
$ git clone https://github.com/blobtoolkit/viewer
$ cd viewer
$ npm install
$ cd ..
Create a Snakemake environment using Conda.
$ conda create -n snake_env -c bioconda snakemake=5.9.1
$ conda activate snake_env
# optionally install DRMAA Python bindings for cluster execution
$ conda install -c anaconda drmaa
$ git clone https://github.com/blobtoolkit/insdc-pipeline
Make a copy of config.yaml matching your assembly name in your working directory and edit the relevant details to fetch FASTA and FASTQ files for your chosen assembly.
mkdir -p ~/btk_workdir
cp insdc-pipeline/config.yaml ~/btk_workdir/ABPC01.yaml
The example config assumes dependencies have been installed under /home/ubuntu and that (BLAST/Diamond) database files should be saved under /home/ubuntu/databases. Change all file/directory paths to match your system and the locations of the BLAST+ and BlobTools2 executables. Config files for public assemblies can also be generated using the script insdc_assemblies_to_config.py.
keep_intermediates: trueBy default the pipeline deletes intermediate files such as BAM files, to ensure these files are retained for use with other tools, set keep_intermediates to true.
assembly:
accession: GCA_000182075.1
alias: M22
bioproject: PRJNA28815
biosample: SAMN00189351
level: contig
prefix: ABPC01
scaffold-count: 6145
span: 10776755Some key-value pairs in the assembly section are used by the pipeline and/or the viewer and are described below. All entries within this section will be searchable once the dataset is loaded into the BlobToolKit Viewer so arbitrary keys are supported to allow flexibility when used for search.
assembly.accessionis displayed as a secondary dataset identifier in theDatasetspane of the viewer.assembly.levelis used to define the record type and should be set to match the assembly level, i.e.contig,scaffoldorchromosomeassembly.prefixis used as a prefix for filenames and as the dataset primary identifier. It should match the dataset id/accession.assembly.scaffold-countis the number of top-level sequences in the assembly.assembly.spanis the total length of the assembly.
To use a local assembly file, make a copy of the assembly FASTA with a filename matching {assembly.prefix}.fasta in your working directory.
busco:
lineage_dir: /data/test/databases/busco
lineages:
- saccharomycetales_odb9
- saccharomyceta_odb9
- ascomycota_odb9
- dikarya_odb9
- fungi_odb9
- eukaryota_odb9To run BUSCO as part of the pipeline, include a busco section with details of the location of the BUSCO lineage_dir in which lineages should be saved if not already present when the pipeline is run and a list of lineages to run.
reads:
coverage:
max: 100
min: 0.5
paired: []
single:
- [SRR090215, LS454, 79442198, ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR090/SRR090215/SRR090215.fastq.gz]
- [SRR090216, LS454, 86168386, ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/SRR090/SRR090216/SRR090216.fastq.gz]The reads section contains details of the read files to use to calculate coverage statistics. Read sets should be listed in paired or single sections according to the sequencing strategy used. Details of each read set should be entered in an array containing:
filename prefix. For public datasets this should be the run accession. For local datasets it should match a read set filename available in the working directory and the filename suffix must match the pattern used by ENA, i.e..fastq.gz,_1.fastq.gz,_2.fastq.gz,_subreads.fastq.gz.sequencing platformis used to determine the expected filename suffix and to determine the parameters to use for read mapping. Valid values areLS454,ILLUMINA,PACBIO_SMRTandOXFORD_NANOPORE.number of basesis the total number of bases in the read file and is used to estimate coverage. If not known this may be set tonull, or omitted for local files when the fourth field is not required.ftp urlis the remote url of the read file to be downloaded. For paired reads this should be a semicolon-separated list of forward and reverse read file URLs
reads.coverage can be defined to ignore read files with less than coverage.min coverage and subsample read files with greater than coverage.max coverage.
settings:
blast_chunk: 100000
blast_max_chunks: 10
blast_overlap: 500
blobtools2_path: /home/ubuntu/blobtools2
chunk: 1000000
taxonomy: /home/ubuntu/databases/taxdump/
tmp: /tmpThe settings section defines some parameters for running the pipeline including paths to blast+ and BlobTools2 and the path under which to save the NCBI taxdump. Further parameters define the behaviour for splitting sequences into chunks when running blast+ to determine the distribution of taxonomic assignments along sequences longer the blast_chunk bases.
similarity:
databases:
- name: nt
local: /home/ubuntu/databases/ncbi_2019_03
source: ncbi
tool: blast
type: nucl
- name: reference_proteomes
local: /home/ubuntu/databases/uniprot_2019_02
max_target_seqs: 1
source: uniprot
tool: diamond
type: prot
defaults:
evalue: 1e-25
mask_ids: [4930]
max_target_seqs: 10
root: 1
taxrule: bestsumorderThe similarity section contains further parameters to control blast+ and Diamond sequence similarity searches. similarity.defaults are shared across all searches and may be overridden by values within similarity.databases. Apart from modifying paths to match your local system, the main parameters to change are:
evalueandmax_target_seqsto control the stringency of the search with the matchingblast+/Diamondparametersmask_idsis a set of taxa to mask from theNCBIorUniProtdatabases, this can be left blank to search the whole databse but for public assemblies consider setting this to the taxon ID of the target genus to avoid hits to self or to very closely related organisms when assigning taxonomy.
taxon:
name: Saccharomyces cerevisiae M22
taxid: 538975While the only required keys for the taxon section are taxon.name and taxon.taxid, all entries in in this section will be searchable once the dataset is loaded into the BlobToolKit Viewer. Full taxonomic information will be added to this section during pipeline execution.
When the pipeline is run, Snakemake will create Conda environments based on the files in the envs/ directory. Due to the way that some Conda recipes are written, it may be necessary to add the following entry to a .condarc file:
path_conflict: warn
conda activate snake_env
BTKDIR=`pwd`/insdc-pipeline
cd $BTKDIR
CORES=32
WORKDIR=~/btk_workdir
ASSEMBLY=ABPC01
snakemake -p --use-conda --conda-prefix ~/.conda --directory $WORKDIR/ --configfile $WORKDIR/$ASSEMBLY.yaml --stats $ASSEMBLY.snakemake.stats --resources btk=1 -j $CORES
Cluster configuration can be altered using the cluster.yaml file. The example commands below are for an LSF cluster with DRMAA:
conda activate snake_env
BTKDIR=`pwd`/insdc-pipeline
cd $BTKDIR
WORKDIR=~/btk_workdir
MULTICORE=8
MAXCORE=16
ASSEMBLY=ABPC01
CONDA_DIR=$HOME/.conda
THREADS=48
snakemake -p --use-conda \
--conda-prefix $CONDA_DIR \
--directory $WORKDIR \
--configfile $WORKDIR/$ASSEMBLY.yaml \
--cluster-config cluster.yaml \
--drmaa " -o {log}.o \
-e {log}.e \
-R \"select[mem>5000] rusage[mem=5000]\" -M 5000" \
--stats $ASSEMBLY.snakemake.stats \
--resources btk=1 \
-j $THREADS
The BlobDir output of this pipeline contains a set of JSON files and can be validated using the associated JSON-schema. A complete specification and validator for the BlobDir format are available at github.com/blobtoolkit/specification.