https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course
마크다운 공부:
https://theorydb.github.io/envops/2019/05/22/envops-blog-how-to-use-md/
2021-01-04
github 블로그 생성하기.
구글 머신러닝 코스 초기 진입하기.
2021-01-05
선형 회귀 (Linear Regression)
https://wikidocs.net/21670
일단 위 링크의 1번 부분만읽고 구글 ㄱㄱ
2021-01-06
구글 크래시 코스 - 1,2강 듣고 정리
여기에서 배우면 3가지 더 잘 하게 됨.
- 프로그래밍 시간을 줄일 수 있는 도구를 얻게됨.
- '맞춤 설정'으로 각 상황에 맞는 프로그래밍을 더 유동적으로 만들 수 있음.
- '언어'관련 프로그램을 만들때에도 언어를 바꾸기만 하면 작동함.
프로그램으로써 수동으로 할 수 없는 일을 짤 수 있음.
내 프로그램의 속성이 옳다는 것을 증명하기 위해 '논리'를 배움.
보는 시야 자체를 넓히는 것에 집중할 것.
지도 머신러닝
- 모델 학습할때 '라벨' 제공 - 예를 들어, 이메일 스팸 필터링에서 '스팸 또는 스팸 아님' 정도. 이것이 우리가 예측하려는 타겟.
- 특성을 데이터를 표현하는 정보.
- 특성은 해당 이메일에서 추출할 수 있는 어떤 정보든 가져와서 머신러닝 시스템에 나타낼 수 있음.
- 라벨이 없는 예 - 특성 정보가 없는 것들.
- 바로 예측을 하는 모델을 만들 것.
라벨 - '예측하는 항목' (단순 선형 회귀의 y 변수)
ex) 밑의 향후 가격, 사진에 표시되는 동물의 종류, 오디오 클립의 의미 등 무엇이든 라벨이 될 수 있음.
특성 - '입력 변수' (단순 선형 회귀의 x 변수)
ex) 간단한 머신러닝 프로젝트에서는 특성을 한 개만 사용하지만 복잡한 프로젝트의 경우 수백만 개의 특성을 사용할 수 있음. x1, x2, x3... xN 이렇게.
특성의 예로는 이메일 텍스트의 단어, 보내는 사람의 주소, 이메일이 전송된 시간, '특정 구문'이 포함된 이메일.
그러니까 특성은 꺼내올 수 있는 대상이고 라벨은 예측하는 대상이다.
모델을 학습 시키려면 '라벨이 있는 예'를 사용할 것.
스팸 감지 예시에서는 사용자가 '스팸 또는 스팸 아님'으로 명시해준 이메일들이 그 예가 됨. 라벨이 있는 것에서 없는 것을 예측하는게 머신 러닝이다.
모델 - 모델이란 특성과 라벨의 관계를 정의하는 것. 예를 들어 스팸 감지 모델에서, 특정 특성과 스팸을 긴밀하게 연결하는 것.
학습 - 모델을 만들거나 배우는 것. 라벨이 있는 예를 모델에 보여주고, 모델이 특성과 라벨의 관계를 점차적으로 학습하게 하는 것.
추론 - 학습된 모델을 라벨이 없는 예에 적용하는 것. 학습된 모델로, 유용한 예측 (y')를 해낸다.
회귀 - 연속적인 값을 예측. 예를 들어, 캘리포니아의 주택 가격이 얼마인가? 사용자가 이 광고를 클릭할 확률이 얼마인가?
분류 - 불연속적인 값을 예측. 예를 들어, 주어진 이메일 메세지가 스팸인가 아닌가. 이 이미지가 강아지인가 고양이인가.
사용자가 '좋아'하는게 아닌, '설명 클릭 횟수'같은게 쓸모있는 것임.
Real basics of machine learning are comprised of labels, features, and models.
In general, machine learning systems are "taught" to use various kinds of inputs in producing socially useful predictions about numerous sets of data.
There are two sets of fundamental terminologies in machine learning: 1) labels and 2) features.
These two terms comprise of what is known as linear regression. Linear regression normally shows the relationship between x- and y- variables. For example, the longer the distance you run, the higher the amount of water you will want to drink. Mathematically, this can be thought of as the value of an independent variable (x) affecting the value of a dependent variable (y). A simple linear regression models this relationship between x- and y- variables. This is where the machine learning principle lies.
Labels: These are the things that we predict: the result values of y. It can be literally anything.
Features: These are the inputs, or the x- variables. Usually, a complex machine learning system consists of millions of kinds of features.
Examples: These are the particular (usually numerical) types of real data, x. X is a vector. There are two types of examples we consider, which are 1) labeled examples and 2) unlabeled examples.
- Labeled examples: Has BOTH feature and the label. To express this in mathematical terms: {features, label}: (x, y). We use these exampels to train the model, just like we use past data to predict outcomes for the future.
- Unlabeled examples: Has ONLY feature and NOT the label. To express this in mathematical terms: {features, ?}: (x, ?). The trained model (using labeled examples) is used to predict the label on unlabeled exampeles.
Models: This is the relationship between features and labels. For example, a spam detection model might associate certain features strongly with "spam". A training process helps the model figure out the relationship or the correlation between features and labels. An inference from the model (which was done through training) applys the model to unlabeled examples, helping us to figure out the labels for those examples.
y=mx+n 이런 고등학교 에서 배운 일차방정식 그래프에서 썼던 m이 이제
y=wx+B로 표현된다. w는 벡터의 가중치이다. b는 편향.
손실이라는 개념을 떠올려보자. 예측값 x에서 실제값을 빼면 손실을 생각할 수 있다. 손실은 항상 양수이다.
손실을 계산하는데에 좋은 함수들이 많지만 그 중에서도 L2 손실이 좋다. 이는 제곱 오차라고도 한다.
예측과 라벨 간의 차이 제곱 = (관찰-예측)^2 = (y-y')^2
모델을 학습 시킬 때에는 하나의 데이터 세트가 아닌 여러 세트를 사용해 손실을 최소화 해야한다. 예측 값이 멀어질 수록 손실도 제곱의 단위로 커진다.

대수학으로는 y = mx + b
머신러닝 관습으로는 y' = b + w1x1
y'는 예측된 라벨(얻고자 하는 출력)이다.
b는 편향 (y절편)이다.
w1은 특성 1의 가중치이다. 가중치는 m으로 표현된 '기울기'와 같은 개념이다.
x1은 특성이다. 즉, 알려진 입력이다.
모델을 학습시킨다는 것은
라벨이 있는 데이터로부터 올바른 가중치와 편향값을 학습(결정)하는 것.
이다.
지도 학습에서 머신러닝 알고리즘은 다양한 예를 검토하고 손실을 최소화하는 모델을 찾아봄으로써 모델을 만들어낸다. 이것을 경험적 위험 최소화 라고 한다.
모델 학습의 목표는, 모든 예에서 평균적으로 작은 손실을 갖는 가중치와 편향의 집합을 찾는 것.

MSE - 평균 제곱 오차
N은 D에 포함된 예의 수이다. MSE는 머신러닝에서 흔히 사용되지만, 모든 상황에서 최선인 유일한 손실 함수는 아니다.
A linear relationship can be drawn when the independent and dependent variables expressed on a grid can be drawn with a straight line. Mathematically, this can be expressed as y = mx +b, where:
- y = value of the label (the value we are trying to predict)
- m = slope of line
- x = value of the input feature
- b = y-intercept
In machine learning, this equation is shaped a little differently in the model. It is y’ = b + w1x1, where:
- y’ = predicted label (desired output)
- b = bias (y-intercept)
- w1 = weight of feature 1
- x1 = value of the input feature (already known)

Inference through the model is done by inserting the value of the features (x1s) into the above equation. A more sophisticated model looks like: y’ = b + w1x1 + w2x2 + w3x3.
Training, as aforementioned, is the process of teaching the model the relationship between features and labels through good values.
Supervised learning, however, is the process of building a model that minimizes loss – empirical risk minimization.
Loss: a number indicating how bad the model’s prediction was on a single example
We don’t need more losses, so the ultimate goal of training a model is finding weights and biases that have low loss, so empirical risk minimization can occur.
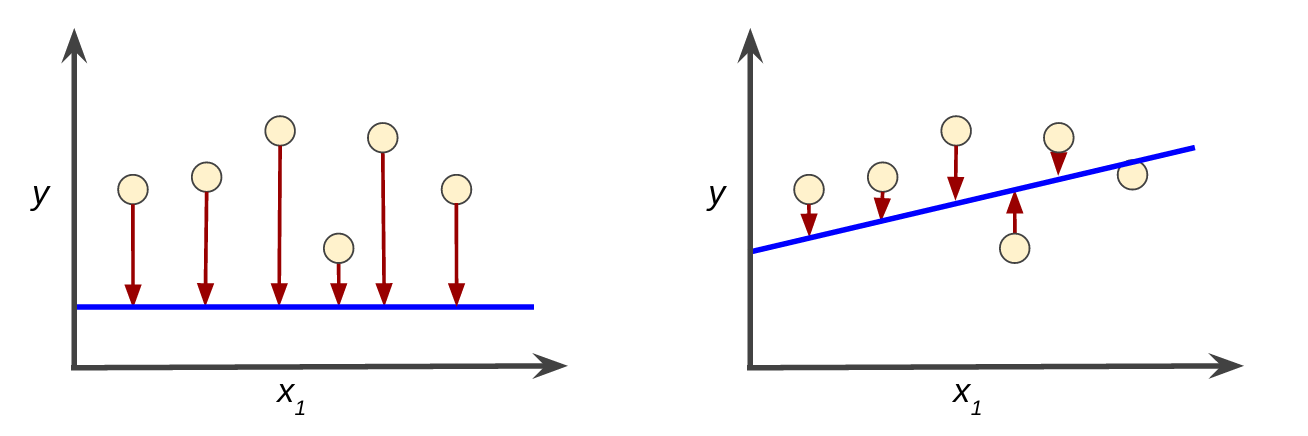
The most popular loss function is squared loss, or L2 loss. It is basically the square of the difference between the label and the prediction. Mathematically, the equation is (observation – prediction(x))2.
Mean square error(MSE) is the average value of the squared loss over the whole data set.
Equation wise it shows this:
Here, prediction(x) is the function that takes into account the weights and biases using the features x.
손실이 줄어드는 방향으로 경사를 계산해야 한다. 모델 매개변수를 감안한 손실 함수의 도함수인 셈이다.
제곱 손실처럼 간단한 손실 함수의 도함수는 계산하기 쉬움.
이차함수를 생각해보면, 어디서 출발하든 결국은 마지막 꼭지에 닿는다. 그러나, 머신러닝에서는 이차함수같이 단순한 경우가 별로 없다.
예고 (foreshadowing): 신경망에선, 그룻 모양과 다르게 최소값이 둘 이상 있고, 초기값에 따라 크게 달라진다.
이게 머신러닝 알고리즘이 시행착오 과정을 겪는 모습이다.
전체 손실이 변하지 않거나 매우 느리게 변할 때까지 계속 반복한다. 이때 모델이 수렴했다고 말한다.
볼록 문제(이차함수)에는 손실 대 가중치 도표가 산출된다. 볼록 문제에서는 기울기가 정확히 0인 지점인 최소값이 하나만 존재하지만, 머신러닝에서는 이보다 더 효율적인 경사하강법을 사용한다.
경사하강법에서도 시작점은 그리 중요하지 않다. 그래서 많은 알고리즘에서 w1을 0, 혹은 랜덤값으로 설정한다.
단일 가중치에 대한 손실의 기울기는 미분 값과 같다.
기울기는 항상 손실 함수 값이 가장 크게 증가하는 방향을 말한다.
경사하강법 알고리즘은 가능한 한 빨리 손실을 줄이기 위해 기울기의 반대 방향으로 이동한다.
경사하강법 알고리즘은 기울기에 학습률 또는 **보폭**이라 불리는 스칼라를 곱해 다음 지점을 결정한다.
ex) 기울기: 2.5 학습률 0.01 -> 이전 지점으로부터 0.025 떨어진 지점이 다음 지점이다.
초매개변수는 프로그래머가 머신러닝 알고리즘에서 조정하는 값.
대부분 상황에서는 학습률을 미세 조정하는데 상당한 시간을 소비한다.
학습률을 너무 작게 설정하면 학습 시간이 매우 오래 걸릴 것.
반대로 크게 설정하면 최저점을 무질서하게 이탈할 우려.
모든 회귀 문제에는 골디락스 학습률이 있다.
이는 손실 함수가 얼마나 평탄한지 여부와 관련이 있다.
배치는 경사하강법에서 단일 반복에서 기울기를 계산하는 데 사용하는 예의 총 개수이다.
배치가 지금까지는 전체 데이터 세트라고 했지만 이것은 너무 커질 수도 있는 일이다.
무작위로 데이터 세트에서 예를 선택하면 훨씬 적은 데이터 세트로 중요한 평균값을 추정할 수 있다.
확률적 경사하강법은 이 아이디어를 더욱 확장한 것으로서, 반복당 하나의 예만을 사용한다. 이는 노이즈가 매우 심하다.
미니 배치 확률적 경사하강법은 위 둘 방법간의 절충안이다. 노이즈는 줄이면서 전체 배치보다는 효율적이다.
텐서플로우 도구함의 계층 구조 이미지
높은 수준의 API일수록 구현하기 쉽고 유연함이 떨어진다.
import tensorflow as tf
# Set up a linear classifier.
classifier = tf.estimator.LinearClassifier()
# Train the model on some example data.
classifier.train(input_fn=train_input_fn, steps=2000)
# Use it to predict.
predictions = classifier.predict(input_fn=predict_input_fn)이런 식이다 ㅇㅇ
확률적 경사하강법의 성능에 악영향을 줄 수 있는 의도치 않은 정렬 효과를 방지하고자 데이터를 무작위로 추출.
california_housing_dataframe = california_housing_dataframe.reindex(
np.random.permutation(california_housing_dataframe.index))
# 랜덤으로 뽑음.
california_housing_dataframe["median_house_value"] /= 1000.0
# 학습률이 일반적인 범위로 들어오게 하기 위해서 천 단위로 만들어줌.
california_housing_dataframe각 특성에 들어있는 데이터 유형을 지정해야 한다. 이 실습과 이후 실습에서는 주로 2가지 데이터 유형을 사용한다.
- 범주형 데이터: 텍스트로 이루어진 데이터.
- 수치 데이터: 정수 또는 부동 소수점 숫자이며 숫자로 취급하는 데이터. 우편번호같은건 범주형으로 취급하는 경우도 있음.
특성열이라는 열을 만듦. 데이터 자체는 저장하지 않고, 데이터의 형식 (설명)만 저장함.
다음으로는 LinearRegressor를 사용하여 선형 회귀 모델을구성합니다. 미니 배치 확률적 경사하강법(SGD)을 구현하는 GradientDescentOptimizer를 사용하여 이 모델을 학습시킬 것입니다. learning_rate 인수는 경사 단계의 크기를 조절합니다.
참고: 안전을 위해 옵티마이저에 clip_gradients_by_norm을 통해 경사 제한을 적용합니다. 경사 제한은 학습 중에 경사가 너무 커져서 경사하강법이 실패하는 경우가 나타나지 않도록 제한합니다.
판다스가 안되니까 뭘 못하겠다.. pandas, numpy를 우선적으로 마스터하고 가자.


