graphblas-algorithms is a collection of GraphBLAS algorithms written using
python-graphblas.
It may be used directly or as an experimental
backend to NetworkX.
Why use GraphBLAS Algorithms? Because it is fast, flexible, and familiar by using the NetworkX API.
Are we missing any algorithms that you want?
Please let us know!
conda install -c conda-forge graphblas-algorithms
pip install graphblas-algorithms
First, create a GraphBLAS Matrix.
import graphblas as gb
M = gb.Matrix.from_coo(
[0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 3],
[1, 3, 0, 0, 1, 2],
[1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6.],
nrows=4, ncols=4, dtype='float32'
)Next wrap the Matrix as ga.Graph.
import graphblas_algorithms as ga
G = ga.Graph(M)Finally call an algorithm.
hubs, authorities = ga.hits(G)When the result is a value per node, a gb.Vector will be returned.
In the case of HITS,
two Vectors are returned representing the hubs and authorities values.
Algorithms whose result is a subgraph will return ga.Graph.
Dispatching to plugins is a new feature in Networkx 3.0.
When both networkx and graphblas-algorithms are installed in an
environment, calls to NetworkX algorithms can be dispatched to the
equivalent version in graphblas-algorithms.
import networkx as nx
import graphblas_algorithms as ga
# Generate a random graph (5000 nodes, 1_000_000 edges)
G = nx.erdos_renyi_graph(5000, 0.08)
# Explicitly convert to ga.Graph
G2 = ga.Graph.from_networkx(G)
# Pass G2 to NetworkX's k_truss
T5 = nx.k_truss(G2, 5)G2 is not a nx.Graph, but it does have an attribute
__networkx_plugin__ = "graphblas". This tells NetworkX to
dispatch the k_truss call to graphblas-algorithms. This link
connection exists because graphblas-algorithms registers
itself as a "networkx.plugin" entry point.
The result T5 is a ga.Graph representing the 5-truss structure of the
original graph. To convert to a NetworkX Graph, use:
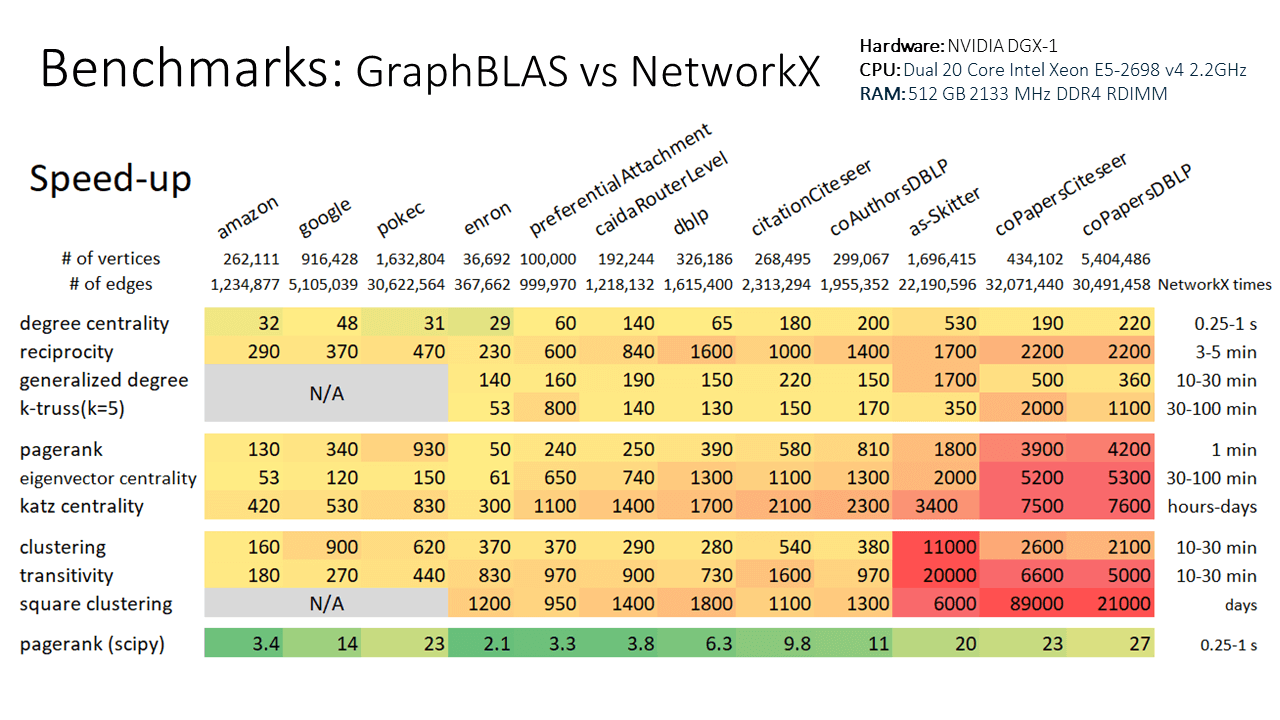
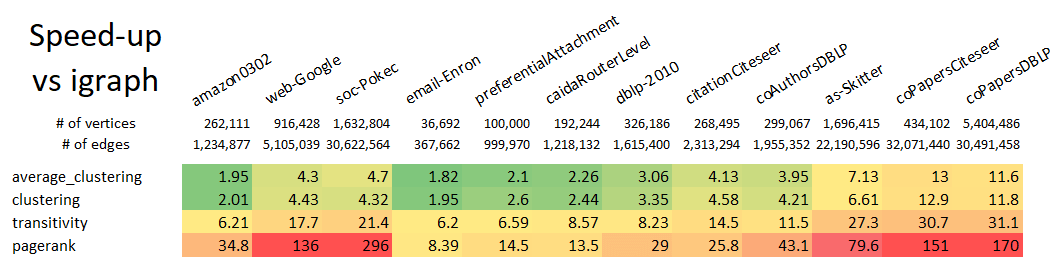
T5.to_networkx()Note that even with the conversions to and from ga.Graph, this example still runs 10x
faster than using the native NetworkX k-truss implementation. Speed improvements scale
with graph size, so larger graphs will see an even larger speed-up relative to NetworkX.
The following NetworkX algorithms have been implemented by graphblas-algorithms and can be used following the dispatch pattern shown above.
graphblas_algorithms.nxapi
├── boundary
│ ├── edge_boundary
│ └── node_boundary
├── centrality
│ ├── degree_alg
│ │ ├── degree_centrality
│ │ ├── in_degree_centrality
│ │ └── out_degree_centrality
│ ├── eigenvector
│ │ └── eigenvector_centrality
│ └── katz
│ └── katz_centrality
├── cluster
│ ├── average_clustering
│ ├── clustering
│ ├── generalized_degree
│ ├── square_clustering
│ ├── transitivity
│ └── triangles
├── community
│ └── quality
│ ├── inter_community_edges
│ └── intra_community_edges
├── components
│ ├── connected
│ │ ├── is_connected
│ │ └── node_connected_component
│ └── weakly_connected
│ └── is_weakly_connected
├── core
│ └── k_truss
├── cuts
│ ├── boundary_expansion
│ ├── conductance
│ ├── cut_size
│ ├── edge_expansion
│ ├── mixing_expansion
│ ├── node_expansion
│ ├── normalized_cut_size
│ └── volume
├── dag
│ ├── ancestors
│ └── descendants
├── dominating
│ └── is_dominating_set
├── efficiency_measures
│ └── efficiency
├── generators
│ └── ego
│ └── ego_graph
├── isolate
│ ├── is_isolate
│ ├── isolates
│ └── number_of_isolates
├── isomorphism
│ └── isomorph
│ ├── fast_could_be_isomorphic
│ └── faster_could_be_isomorphic
├── linalg
│ ├── bethehessianmatrix
│ │ └── bethe_hessian_matrix
│ ├── graphmatrix
│ │ └── adjacency_matrix
│ ├── laplacianmatrix
│ │ ├── laplacian_matrix
│ │ └── normalized_laplacian_matrix
│ └── modularitymatrix
│ ├── directed_modularity_matrix
│ └── modularity_matrix
├── link_analysis
│ ├── hits_alg
│ │ └── hits
│ └── pagerank_alg
│ ├── google_matrix
│ └── pagerank
├── lowest_common_ancestors
│ └── lowest_common_ancestor
├── operators
│ ├── binary
│ │ ├── compose
│ │ ├── difference
│ │ ├── disjoint_union
│ │ ├── full_join
│ │ ├── intersection
│ │ ├── symmetric_difference
│ │ └── union
│ └── unary
│ ├── complement
│ └── reverse
├── reciprocity
│ ├── overall_reciprocity
│ └── reciprocity
├── regular
│ ├── is_k_regular
│ └── is_regular
├── shortest_paths
│ ├── dense
│ │ ├── floyd_warshall
│ │ ├── floyd_warshall_numpy
│ │ └── floyd_warshall_predecessor_and_distance
│ ├── generic
│ │ └── has_path
│ ├── unweighted
│ │ ├── all_pairs_shortest_path_length
│ │ ├── single_source_shortest_path_length
│ │ └── single_target_shortest_path_length
│ └── weighted
│ ├── all_pairs_bellman_ford_path_length
│ ├── bellman_ford_path
│ ├── bellman_ford_path_length
│ ├── negative_edge_cycle
│ └── single_source_bellman_ford_path_length
├── simple_paths
│ └── is_simple_path
├── smetric
│ └── s_metric
├── structuralholes
│ └── mutual_weight
├── tournament
│ ├── is_tournament
│ ├── score_sequence
│ └── tournament_matrix
├── traversal
│ └── breadth_first_search
│ ├── bfs_layers
│ └── descendants_at_distance
└── triads
└── is_triad






