BPE is a Business Process Engine that brings BPMN to Erlang and Erlang to Enterprises. It provides infrastructure for Workflow Definitions, Process Orchestration, Rule Based Production Systems and Distributed Storage.
iex(1)> {_,p} = :bpe.start :bpe_xml.def, []
{:ok, '76900759556000'}
iex(2)> :bpe.next p
{:complete, 'either'}
iex(3)> :bpe.next p
{:complete, 'left'}
iex(4)> :bpe.next p
{:complete, 'right'}
iex(5)> :bpe.next p
{:complete, 'join'}
iex(6)> :bpe.next p
{:complete, 'join'}
iex(7)> :bpe.next p
{:complete, 'epilog'}
iex(8)> :bpe.next p
{:complete, 'finish'}
iex(9)> :bpe.next p
:Final
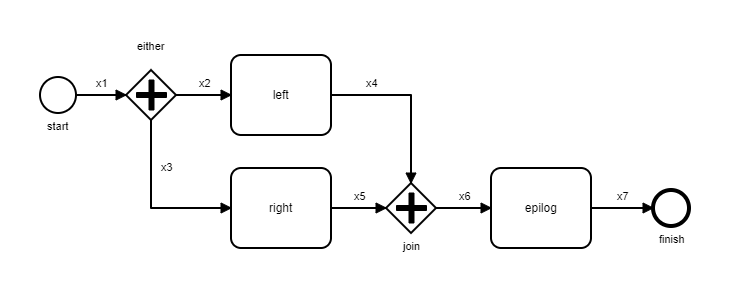
> :kvs.all '/bpe/flow/77012724426000'
[
{:sched, {:step, 0, '77012724426000'}, 1, ['x1']},
{:sched, {:step, 1, '77012724426000'}, 1, ['x2', 'x3']},
{:sched, {:step, 2, '77012724426000'}, 2, ['x4', 'x3']},
{:sched, {:step, 3, '77012724426000'}, 1, ['x4', 'x5']},
{:sched, {:step, 4, '77012724426000'}, 1, ['x5']},
{:sched, {:step, 5, '77012724426000'}, 1, ['x6']},
{:sched, {:step, 6, '77012724426000'}, 1, ['x7']},
{:sched, {:step, 7, '77012724426000'}, 1, []}
]
Processes are main entities of BPE, they map one-to-one to Erlang processes. Basically, BPE process is an algorithm or function, that is executed entirely in the context of Erlang process. The arguments for such algorithms are: values from infinite streams (KVS chains); values from Erlang messages being sent to BPE process.
-record(step, { id = 0 :: integer(), proc = "" :: list() }).
-record(role, { id = [] :: list(), name :: binary(), tasks = [] :: term() }).
-record(sched, { id = [] :: [] | #step{},
prev=[] :: [] | integer(),
next=[] :: [] | integer(),
pointer = -1 :: integer(),
state = [] :: list(list()) }).
-record(hist, { id = [] :: [] | #step{},
prev=[] :: [] | integer(),
next=[] :: [] | integer(),
name=[] :: [] | binary() | list(),
task=[] :: [] | atom() | list() | #sequenceFlow{} | condition(),
docs=[] :: list(tuple()),
time=[] :: [] | #ts{} }).
-record(process, { id = [] :: procId(),
prev=[] :: [] | integer(),
next=[] :: [] | integer(),
name=[] :: [] | binary() | string() | atom(),
feeds=[] :: list(),
roles = [] :: term(),
tasks = [] :: list(tasks()),
events = [] :: list(events()),
flows = [] :: list(#sequenceFlow{}),
docs = [] :: list(tuple()),
options = [] :: term(),
module = ?DEFAULT_MODULE :: [] | atom(),
xml = [] :: list(),
timer = [] :: [] | reference(),
notifications=[] :: [] | term(),
result = [] :: [] | binary(),
started = [] :: [] | #ts{},
beginEvent = [] :: list() | atom(),
endEvent = [] :: list() | atom() }).During execution of the process, all steps are being written to the persistent storage,
by which execution logic is restorable and reproducible. The process definition is actually
diagram or graph where points represented by task and edges by sequenceFlow.
The step itself is represented as task (point). The transition between steps is
represented as sequenceFlow (edge).
-define(TASK, id=[] :: list(),
name=[] :: list() | binary(),
in=[] :: list(list()),
out=[] :: list(list()),
prompt=[] :: list(tuple()),
roles=[] :: list(atom()),
etc=[] :: list({term(),term()}) ).
-record(beginEvent , { ?TASK }).
-record(endEvent, { ?TASK }).
-record(task, { ?TASK }).
-record(userTask, { ?TASK }).
-record(serviceTask, { ?TASK }).
-record(receiveTask, { ?TASK, reader=[] :: #reader{} }).
-record(sendTask, { ?TASK, writer=[] :: #writer{} }).The history record of process execution is
represented as hist and captures the sequenceFlow information.
-type condition() :: {compare,BpeDocParam ::
{ atom(),
term()},
Field :: integer(),
ConstCheckAgainst :: term()
}
| {service,atom()}.
-record(sequenceFlow, { id=[] :: list(),
name=[] :: list() | binary(),
condition=[] :: [] | condition() | binary(),
source=[] :: list(),
target=[] :: list(integer()) | list(list()) }).While Tasks are deterministic, where you're getting a new task from previous one, the Events are non-deterministic, where you could get a new task by external event from the system to the process.
-define(EVENT, id=[] :: list() | atom(),
name=[] :: list() | binary(),
prompt=[] :: list(tuple()),
etc=[] :: list({term(),term()}),
payload=[] :: [] | binary(),
timeout=[] :: [] | #timeout{} ).
-define(CYCLIC, timeDate=[] :: [] | binary(),
timeDuration=[] :: [] | binary(),
timeCycle=[] :: [] | binary() ).
-record(messageEvent, { ?EVENT }).
-record(messageBeginEvent, { ?EVENT }).
-record(boundaryEvent,{ ?EVENT, ?CYCLIC }).
-record(timeoutEvent, { ?EVENT, ?CYCLIC }).Gateways represent multiplexors and demultiplexors which cause non-linear trace and multiple current states as leaves of execution graph.
-type gate() :: exclusive | parallel | inclusive | complex | event.
-record(gateway, { ?TASK, type= parallel :: gate() }).Full set of BPMN 2.0 fields could be obtained at http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/2.0, page 3-7.
(bpe@127.0.0.1)1> rr(bpe).
[beginEvent,container,endEvent,history,id_seq,iterator,
messageEvent,process,sequenceFlow,serviceTask,task,userTask]
(bpe@127.0.0.1)2> bpe:start(spawnproc:def(),[]).
bpe_proc:Process 39 spawned <0.12399.0>
{ok,<0.12399.0>}
(bpe@127.0.0.1)3> bpe:complete(39).
(bpe@127.0.0.1)4> bpe:complete(39).
(bpe@127.0.0.1)5> bpe:complete(39).
(bpe@127.0.0.1)5> bpe:hist(39).
[#history{id = 28,version = undefined,container = feed,
feed_id = {history,39},
prev = 27,next = undefined,feeds = [],guard = true,
etc = undefined,name = "Order11",
task = {task,"end"}},
#history{id = 27,version = undefined,container = feed,
feed_id = {history,39},
prev = 26,next = 28,feeds = [],guard = true,etc = undefined,
name = "Order11",
task = {task,"end2"}},
#history{id = 26,version = undefined,container = feed,
feed_id = {history,39},
prev = undefined,next = 27,feeds = [],guard = true,
etc = undefined,name = "Order11",
task = {task,"begin"}}]Instantiation of process means creating persistent context of document flow.
load(ProcName)
start(Proc,Docs)
amend(Proc,Docs)
complete(Proc)
history(ProcId)
task(Name,Proc)
doc(Name,Proc)
events(Proc)
tasks(Proc)Using 'tasks' API you can fetch current documents attached to the given process at particular stage. Using 'amend' API you can upload or change document at current stage. 'push' API moves current stage documents further by workflow.
Let us see how we could create initial 'Wire Transfer' transaction:
> rr(bpe).
[ beginEvent,boundaryEvent,container,endEvent,history,id_seq,
interval,iterator,kvs,log,messageEvent,operation,process,
receiveTask,sequenceFlow,serviceTask,task,timeoutEvent,userTask ]
> rr(kvs).
[column,config,container,id_seq,interval,iterator,kvs,log,
operation,query,schema,table,user,user2]
> Proc = bpe:load(39).
> bpe:tasks(Proc).
[#userTask{name = 'Init',roles = [], module = spawnproc},
#userTask{name = 'Signatory',roles = [], module = spawnproc},
#serviceTask{name = 'Payment',roles = [], module = spawnproc},
#serviceTask{name = 'Process',roles = [], module = spawnproc},
#endEvent{name = 'Final',module = []}]
> bpe:docs(Proc).
[]
> bpe:amend(39,[{'WireTransfer',#user{id=1},#user{id=2}}]).
> bpe:docs(bpe:load(39)).- Maxim Sokhatsky
- Oleksandr Naumov
- Ivan Kulyk
OM A HUM