C++ implementation of random forests
详细说明请前往CSDN Random Forests C++实现:细节,使用与实验
- 适用于分类和回归,支持回归的多维输出(multi-target regression)
- 支持3种随机性
- off-the-shelf,即插即用
- 支持特征重要性评估
- 支持计算proximity和离群点检测
- 可保存训练完成的模型至本地 (XML格式,可读性强),也可读取本地模型进行预测*
(使用tinyxml2库支持xml文件的读写)
从本地数据文件读入数据集进行训练,计算oob-error(oob-mse),并保存forest到本地。 本地训练文件格式(dataset files for trainning):
分类(classification)
@totoal_sample_num=19020
@variable_num=10
@class_num=2
1 86.088 36.259 3.4839 0.2359 0.1337 -12.893 -56.746 -4.0291 4.158 372.98
1 76.099 18.755 2.8639 0.3461 0.2209 -90.721 -52.015 -19.577 3.46 271.43
1 62.989 22.083 3.1191 0.2258 0.1167 -85.779 48.038 19.251 7.652 246
1 19.55 10.763 2.3201 0.6077 0.3421 8.3626 -17.38 -10.092 17.368 173.39
0 67.609 26.678 2.632 0.3851 0.2462 -56.63 -57.963 19.806 79.666 227.19
1 24.909 17.432 2.632 0.3944 0.2229 7.1171 -2.3838 -8.6055 37.114 204.79
... ...
回归(regression)
@totoal_sample_num=4177
@variable_num_x=8
@variable_num_y=1
15 1 0.455 0.365 0.095 0.514 0.2245 0.101 0.15
7 1 0.35 0.265 0.09 0.2255 0.0995 0.0485 0.07
9 2 0.53 0.42 0.135 0.677 0.2565 0.1415 0.21
10 1 0.44 0.365 0.125 0.516 0.2155 0.114 0.155
7 3 0.33 0.255 0.08 0.205 0.0895 0.0395 0.055
8 3 0.425 0.3 0.095 0.3515 0.141 0.0775 0.12
... ...
(1)分类森林(classification forest)
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#include "RandomCLoquatForests.h"
#include "UserInteraction2.h"
int main()
{
// read training samples if necessary
char filename[500] = "./DataSet/Classification/pendigits.tra";
float** data = NULL;
int* label = NULL;
Dataset_info_C datainfo;
InitalClassificationDataMatrixFormFile2(filename, data/*OUT*/, label/*OUT*/, datainfo/*OUT*/);
// setting random forests parameters
RandomCForests_info rfinfo;
rfinfo.datainfo = datainfo;
rfinfo.maxdepth = 40;
rfinfo.ntrees = 500;
rfinfo.mvariables = (int)sqrtf(datainfo.variables_num);
rfinfo.minsamplessplit = 5;
rfinfo.randomness = 1;
// train forest
LoquatCForest* loquatCForest = NULL;
TrainRandomForestClassifier(data, label, rfinfo, loquatCForest /*OUT*/, 50);
float error_rate = 1.f;
OOBErrorEstimate(data, label, loquatCForest, error_rate /*OUT*/);
// save RF model, 0:xml, 1:plain text
SaveRandomClassificationForestModel("Modelfile.xml", loquatCForest, 0);
// clear the memory allocated for the entire forest
ReleaseClassificationForest(&loquatCForest);
// release money: data, label
for (int i = 0; i < datainfo.samples_num; i++)
delete[] data[i];
delete[] data;
delete[] label;
return 0;
}(2)回归森林(regression forest)
#include "RandomRLoquatForests.h"
#include "UserInteraction2.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// read training samples if necessary
char filename[500] = "./DataSet/Regression/Housing_Data_Set-R.txt";
float** data = NULL;
float* target = NULL;
Dataset_info_R datainfo;
InitalRegressionDataMatrixFormFile2(filename, data /*OUT*/, target /*OUT*/, datainfo /*OUT*/);
// setting random forests parameters
RandomRForests_info rfinfo;
rfinfo.datainfo = datainfo;
rfinfo.maxdepth = 40;
rfinfo.ntrees = 200;
rfinfo.mvariables = (int)(datainfo.variables_num_x / 3.0 + 0.5);
rfinfo.minsamplessplit = 5;
rfinfo.randomness = 1;
rfinfo.predictionModel=PredictionModel::constant;
// train forest
LoquatRForest* loquatRForest = NULL;
TrainRandomForestRegressor(data, target, rfinfo, loquatRForest /*OUT*/, false, 20);
float* mean_squared_error = NULL;
MSEOnOutOfBagSamples(data, target, loquatRForest, mean_squared_error /*OUT*/);
delete[] mean_squared_error;
// save RF model, 0:xml, 1:plain text
SaveRandomRegressionForestModel("testModelfile-R.xml", loquatRForest, 0);
// clear the memory
ReleaseRegressionForest(&loquatRForest);
// release money: data, target
for (int i = 0; i < datainfo.samples_num; i++)
delete[] data[i];
delete[] data;
delete[] target;
return 0;
}说明
- 以上代码仅为主干,实际使用需对函数返回值进行判断。
- RF结构体对象loquatForest的内存由TrainRandomForestClassifier /TrainRandomForestRegressor 负责分配,由ReleaseClassificationForest /ReleaseRegressionForest 释放内存,用户无需对其分配或者释放
- OOBErrorEstimate 计算out-of-bag分类错误率,输入参数data, label必须与训练时相同,MSEOnOutOfBagSamples类同
- InitalClassificationDataMatrixFormFile2/InitalRegressionDataMatrixFormFile2 从本地文件读取数据集。也可以自行准备训练数据,就可以不调用上述函数。
数据集
| 名称 | 分类/回归 | 来源 | 样本数 | 特征数 | 类别数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chess-krvk | classification | UCI | 28056 | 6 | 18 |
| Gisette | classification | UCI | 6000/1000 | 5000 | 2 |
| ionosphere | classification | UCI | 351 | 34 | 2 |
| mnist | classification | libsvm | 60000/10000 | 780 | 10 |
| MAGIC_Gamma_Telescope | classification | UCI | 19020 | 10 | 2 |
| pendigits | classification | UCI | 7494/3498 | 16 | 10 |
| spambase | classification | UCI | 4601 | 57 | 2 |
| Sensorless_drive_diagnosis | classification | UCI | 58509 | 48 | 11 |
| Smartphone Human Activity Recognition | classification | UCI | 4242 | 561 | 6 |
| waveform | classification | UCI | 5000 | 40 | 3 |
| satimage | classification | UCI | 6435 | 36 | 6 |
| Car Evaluation | classification | UCI | 1728 | 6 | 4 |
| sonar | classification | UCI | 208 | 60 | 2 |
| abalone | regression | UCI | 4177 | 8 | —— |
| airfoil_self_noise | regression | UCI | 1503 | 5 | —— |
| Bike-Sharing1 | regression | UCI | 17379 | 14 | —— |
| Combined_Cycle_Power_Plant | regression | UCI | 9568 | 4 | —— |
| elevators | regression | openml | 16599 | 18 | —— |
| QSAR fish toxicity | regression | UCI | 908 | 6 | —— |
| Housing | regression | kaggle | 506 | 13 | —— |
| Parkinsons_Telemonitoring2 | regression | UCI | 5875 | 19 | —— |
| Superconductivty | regression | UCI | 21263 | 81 | —— |
| YearPredictionMSD | regression | Million Song Dataset/ UCI |
515345 | 90 | —— |
- Bike-Sharing: 原数据集去掉第1、2列
- Parkinsons_Telemonitoring: 预测输出(output)是2维的。将原数据集第1列(subject number)去掉,UCI网站上记录“Number of Attributes:26”但根据下载的数据集只有22维(包括2维output)
参数
下一小节表格中“参数”列为 [TreesNum, SplitVariables, MaxDepth, MinSamplesSplit] (randomness均为1,即经典RF)。实验并没有对参数进行调优,而是根据经验选取了个人认为比较合理的参数组合。实验目的一方面是为了验证算法实现的正确性,另一方面也想说明RF对参数敏感度较低(相比SVM)。
结果
如果没有特殊说明,分类和回归问题的实验结果分别通过out-of-bag分类错误率(%)和out-of-bag 均方误差(Mean Square Error (MSE))来统计,结果运行10次取平均和标准差。可以看到,大多数数据集都采用了默认的参数,也能达到较理想效果。
| 数据集 | 参数 | oob error(%)/mse | 分类/回归 |
|---|---|---|---|
| chess-krvk | [500, 2*, 40, 5] | 16.46636±0.07493 | C |
| Gisette | [200, 70*, 40, 5] | 2.932105±0.10090(oob) 3.010±0.13333(test set) |
C |
| ionosphere | [200, 5*, 40, 5] | 6.325±0.213 | C |
| mnist | [200, 27*, 40, 5] | 3.307166±0.02863(oob) 3.066±0.0665(test set) |
C |
| MAGIC_Gamma_Telescope | [200, 3*, 40, 5] | 11.8559±0.04347 | C |
| pendigits | [200, 4*, 40, 5] | 0.880822±0.03428(oob) 3.670668±0.049843(test set) |
C |
| spambase | [200, 7*, 40, 5] | 4.514335±0.10331 | C |
| satimage | [500, 6*, 40, 5] | 8.102018±0.057777 | C |
| Sensorless_drive_diagnosis | [200, 6*, 40, 5] | 0.169049±0.009346 | C |
| Smartphone Human Activity Recognition | [200, 23*, 40, 5] | 7.39415±0.1159 | C |
| waveform | [500, 6*, 40, 5] | 14.70493±0.19792 | C |
| Car Evaluation | [200,2*,40,5] | 1.9456±0.11923 | C |
| sonar | [200,7*,40,2] | 14.961±0.8646 | C |
| abalone | [500, 3#, 40, 5] | 4.58272±0.008826 | R |
| airfoil_self_noise | [200, 2/5, 40, 5] | 3.83345±0.034283 | R |
| Bike-Sharing | [500, 5#, 40, 5] | 29.7227±0.84333 | R |
| Combined_Cycle_Power_Plant | [200, 2/4, 40, 5] | 9.94693±0.031153 | R |
| elevators | [200, 10/18, 40, 5] | 7.1859E-06±3.15264E-08 | R |
| QSAR fish toxicity | [200, 2#, 40, 2] | 0.7669898±0.003282 | R |
| Housing | [200, 4#, 40, 5] | 10.077±0.1923 | R |
| Parkinsons_Telemonitoring3 | [200,19,40,5] | [1.437, 2.523]±[0.01706, 0.03033] | R |
| Superconductivty | [200, 27#, 40, 5] | 81.4527±0.2781 | R |
| YearPredictionMSD | [100, 30#, 40, 50] | 83.1219±0.05236 | R |
*: 表示使用分类森林默认的
#:表示使用回归森林默认的
参数影响(parameters)
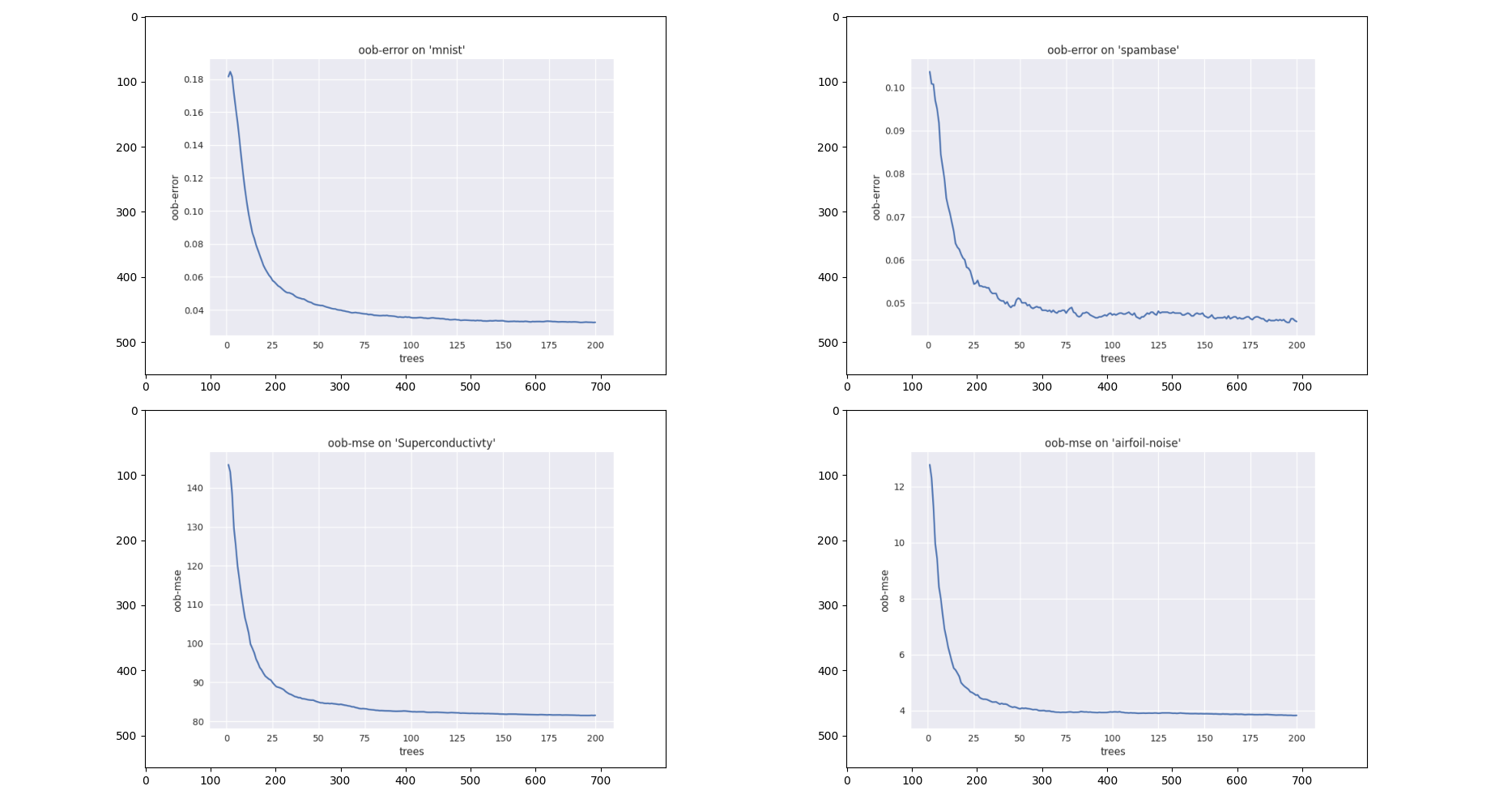
通常RF在默认参数设定下也能取得较理想的效果,通过对参数(见2.2节)调优可以获得更佳的分类/回归效果。一般可以对TreesNum和SplitVariables进行调优。通常认为增加TreesNum会使泛化误差下降(当然也有特例)。如下图,展示了随着树增加,oob error/oob mse呈现下降的趋势。
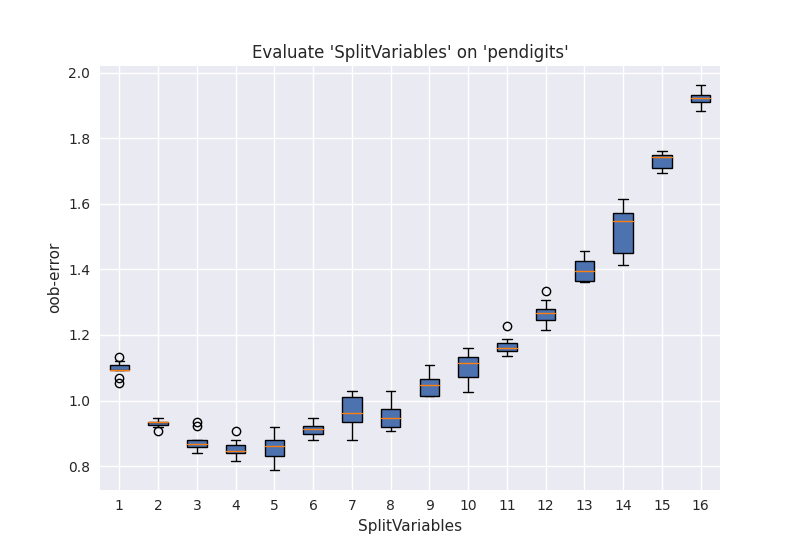
SplitVariables是控制RF随机性的主要参数,当它增加时树之间的关联性也随之增加,而关联性增加会导致分类/回归误差提高[2]。从可调性(Tunability)角度考虑,调节SplitVariables对性能提升的贡献是最大的。而SplitVariables选择默认设定时,通常也能取得不错的效果。下图为pendigits数据集上,不同SplitVariables(样本为16维,TreesNum=500)参数下的分类oob error。
特征重要性(Variable Importance Measurement)
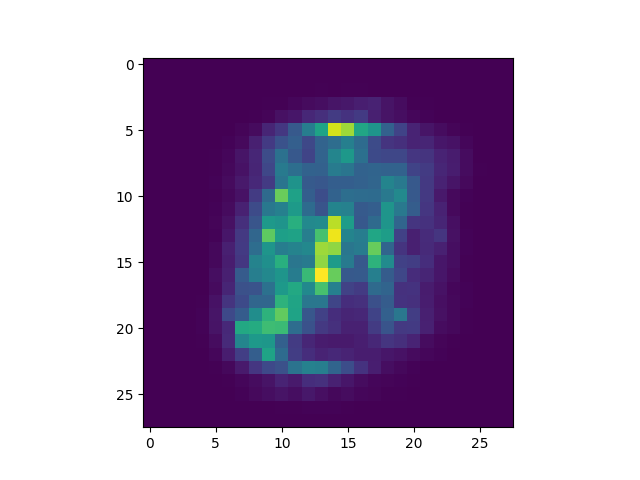
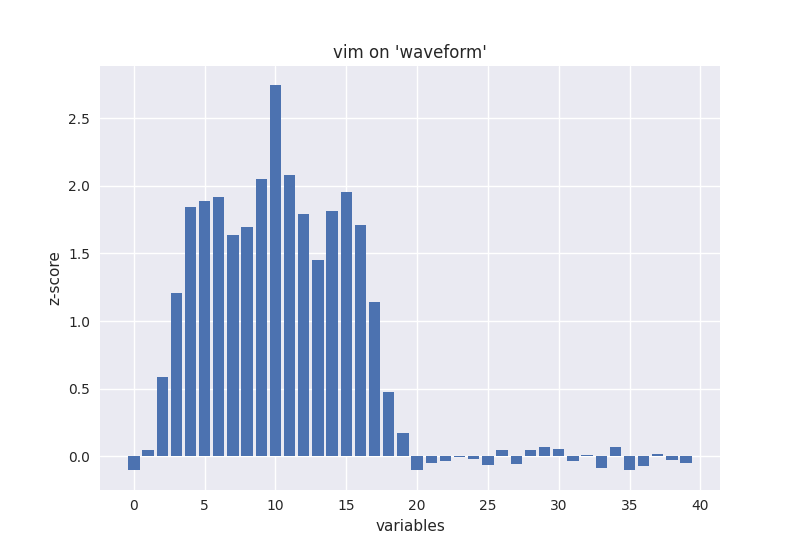
特征重要性(variable importance)的评估是RF“自带”的一个特性。采用oob数据的特征随机交换的方法来估计特征重要性。对于数据集"waveform",结果如下图所示,可见后一半特征的重要性几乎为0,这是因为waveform的后19维特征是随机噪声,因此variable importance计算结果符合上述情况。
使用mnist手写字符识别数据集训练随机森林分类器,样本数60000,特征数780。RF参数为:随机树
多目标回归(Multi-target regression)
这里多目标指的是回归目标是多维的,一般称为multivariate regression或者multi-target regression。可以将多维目标分解为多个单独的回归问题,即可以对每一维输出输出单独训练一个模型,那么输出有
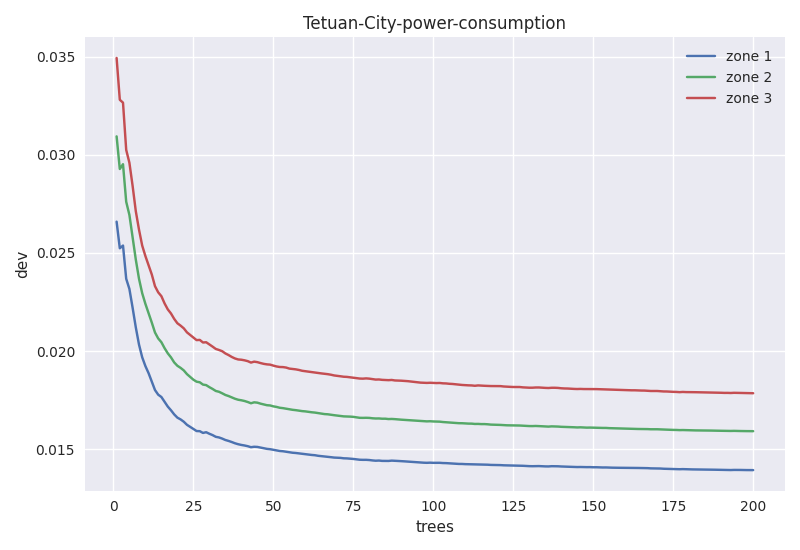
使用Tetuan-City-power-consumption数据集来进行试验,原始数据集是通过时间、温度、湿度、风速等6个变量来预测城市3个配电网的能源消耗,即输入6维,输出3维。由于“时间”变量难以使用,所以分解为[minute,hour,day,month,weekday,weekofyear] 6个变量,加上原始的5个气象变量,形成新的11维输入。RF参数为[200, 3#, 60, 2](参数含义见4.2节)。由于输出具有明确物理含义,且都是正数,衡量回归准备度的指标不再使用oob-mse,而是使用oob样本的平均偏离度