A unified framework for Novel Instance Detection and Segmentation (NIDS).
The basic NIDS-Net does not require any training since it does not involve adapters! It works for one-shot or few-shot detection and segmentation tasks.
Training the adapter is simple and quick because it's just a two-layer network. You can train the adapter in just a few minutes, even with hundreds of epochs!
Novel Instance Detection and Segmentation (NIDS) aims at detecting and segmenting novel object instances given a few examples of each instance. We propose a unified framework (NIDS-Net) comprising object proposal generation, embedding creation for both instance templates and proposal regions, and embedding matching for instance label assignment. Leveraging recent advancements in large vision methods, we utilize the Grounding DINO and Segment Anything Model (SAM) to obtain object proposals with accurate bounding boxes and masks. Central to our approach is the generation of high-quality instance embeddings. We utilize foreground feature averages of patch embeddings from the DINOv2 ViT backbone, followed by refinement through a weight adapter mechanism that we introduce. We show experimentally that our weight adapter can adjust the embeddings locally within their feature space and effectively limit overfitting. This methodology enables a straightforward matching strategy, resulting in significant performance gains. Our framework surpasses current state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating notable improvements of 22.3, 46.2, 10.3, and 24.0 in average precision (AP) across four detection datasets. In instance segmentation tasks on seven core datasets of the BOP challenge, our method outperforms the top RGB methods by 3.6 AP and remains competitive with the best RGB-D method.
FFA is used to generate the initial embeddings in our framework.

Ranked #1: Model-based 2D segmentation of unseen objects – Core datasets.
We prepare demo google colabs: inference on a high-resolution image and Training free one-shot detection.
- Python 3.7 or higher (tested 3.9)
- torch (tested 2.0)
- torchvision
We test the code on Ubuntu 20.04.
git clone https://github.com/YoungSean/NIDS-Net.git
cd NIDS-Net
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate nids
conda install pytorch==2.2.1 torchvision==0.17.1 torchaudio==2.2.1 pytorch-cuda=11.8 -c pytorch -c nvidia
conda install xformers -c xformers
# Assume you have set up the global git email and user name in your git config
# if not, there may be an error when installing the following script
python setup.py install
python -m pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git'
# for using SAM
pip install git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything.git
# Use old supervision.
pip install supervision==0.20.0 Download ViT-H SAM weights
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/segment_anything/sam_vit_h_4b8939.pthAfter installation, there will be a folder named "ckpts". Move the SAM weight to "ckpts/sam_weights/sam_vit_h_4b8939.pth".
mkdir ckpts/sam_weights
mv sam_vit_h_4b8939.pth ckpts/sam_weightsSetting Up 4 Detection Datasets
We do not need training datasets for detectors. We can use template embeddings to train the adapter.This instance-detection repo provide the InsDet-Full.
cd $ROOT
ln -s $HighResolution_DATA databaseWe provide the preprocessed testing images in this link accorinding to this instance-detection. Please put them into "Data" folder as follows:
database
│
└───Background
│
└───Objects
│ │
│ └───000_aveda_shampoo
│ │ │ images
│ │ │ masks
│ │
│ └───001_binder_clips_median
│ │ images
│ │ masks
│ │ ...
│
│
└───Data
│ test_1_all
│ test_1_easy
│ test_1_hard
VoxDet provides the datasets. Save and unzip them in '$ROOT/datasets' to get "datasets/RoboTools", "datasets/lmo", "datasets/ycbv".
You can directly use the demo google colabs: inference on a high-resolution image and Training free one-shot detection.
- Check GroundingDINO and SAM
- GroundingDINO + SAM:
test_gdino_sam.py
- Generate template embeddings via get_object_features_via_FFA.py. Or you can download the template embeddings and model weights for detection datasets. The initial embedding file name includes "object_features". Model weights use the "pth" suffix. Adapted embeddings are saved as JSON files ending with "vitl_reg.json".
You may adjust their filenames to load them in the python scripts.
# download the initial template embeddings of 4 detection datasets
mkdir obj_FFA
wget https://utdallas.box.com/shared/static/50a8q7i5hc33rovgyavoiw0utuduno39 -O obj_FFA/object_features_vitl14_reg.json
mkdir BOP_obj_feat
wget https://utdallas.box.com/shared/static/qlyekivfg6svx84xhh5xv39tun3xza1u -O BOP_obj_feat/lmo_object_features.json
wget https://utdallas.box.com/shared/static/keilpt2i2gk0rrjymg0nkf88bdr734wm -O BOP_obj_feat/ycbv_object_features.json
mkdir RoboTools_obj_feat
wget https://utdallas.box.com/shared/static/e7o7fy00qitmbyg51wb6at9vc1igzupb -O RoboTools_obj_feat/object_features.json
mkdir adapted_obj_feats- Train weight adapters in adapter.py (Optional). You can start with the basic version without the weight adapter.
To train the adapter, prepare the training dataset and set parameters in adapter.py.
After training, use the adapter to refine the embeddings and store them in the folder '$ROOT/adapted_obj_feats'. The adapter.py script can fine-tune the template embeddings using the trained adapter.
If you do not or forget to convert with adapter.py, you can convert original to adapted template embeddings with 'utils/transform_adapted_feats.py', typically used for BOP datasets.
To reuse the adapter during inference, enable "use_adapter" and specify the weight adapter weight path in the inference scripts.
Here's how to train the weight adapter for high-resolution data:
python adapter.py- Inference
# for high-resolution dataset
# demo image
# in each script, there are some parameters you can adjust
# for example, the flag "use_adapter", the adapter type and the adapter weight path in demo_eval_gdino_FFA.py
python demo_eval_gdino_FFA.py
# dataset results
# for high-resolution dataset
python mini_test_eval_gdino_FFA.py
# for lm-o dataset
python lmo_test_eval_gdino_FFA.py
# since YCB-V and RoboTools have many scenes
# we first get detection prediction results for each scene
./get_ycbv_prediction.sh
./get_RoboTools_prediction.sh
# then merge them using utils/merge_COCO_json.py. You can download Ground truth files in the following link.
# evaluate them with eval_result.pyWe include the ground truth files and our predictions in this link. You can run eval_results.py to evaluate them. Ground truth filenames include "gt" or "test", while our prediction filenames include "coco_instances".
Note: Uncomment this line sel_roi['mask'] = mask if you need masks in the result.
Please follow CNOS to download the datasets. Our code is based on CNOS and SAM6D.
We mainly use the template images from BlenderProc4BOP set due to its better performance. The dataest is used to generate template embeddings. Please find the template embeddings in this link. So you can use these template embeddings to train the adapter.
If you just need template embeddings for matching, you do not need to download the BlenderProc4BOP datasets for inference. Only testing datasets are needed.
Inference on BOP datasets
Access NIDS-Net's prediction results, template embeddings and the adapter model weight for seven BOP benchmark datasets here.
Before running the inference, please download the template embeddings and adapter model weight from the link above. You may set self.use_adapter to True and modify the model weight path and the adapted template embedding path in the model file.
- Train the weight adapter. You may change the folder path in the following python scripts. These paths are pointing to initial instance template embeddings.
python obj_adapter.py
# now you train a common adapter for all datasets
# Then you can use the adapter to generate the adapter template embeddings for the BOP datasets
# the following python script will generate the adapter template embeddings.
python transforme_adapter_feats.py- Run NIDS-Net to get predictions of a BOP dataset:
export DATASET_NAME=lmo
# adding CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=$GPU_IDS if you want to use a specific GPU
# with Grounded-SAM + PBR
python run_inference.py dataset_name=$DATASET_NAME
Once the script completes, NIDS-Net will generate a prediction file at this directory. You can then assess the prediction on the BOP Challenge website.
- Prediction Visualization with Detectron2
Display masks, object IDs, and scores using Detectron2.
python -m src.scripts.visualize_detectron2 dataset_name=$DATASET_NAME input_file=$INPUT_FILE output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR
We test our NIDS-Net on YCBV objects using ROS with a Fetch robot. We use
- template embeddings of synthetic images from CNOS: "ros/weight_obj_shuffle2_0501_bs32_epoch_500_adapter_descriptors_pbr.json"
- The adapter weight: "ros/bop_obj_shuffle_weight_0430_temp_0.05_epoch_500_lr_0.001_bs_32_weights.pth"
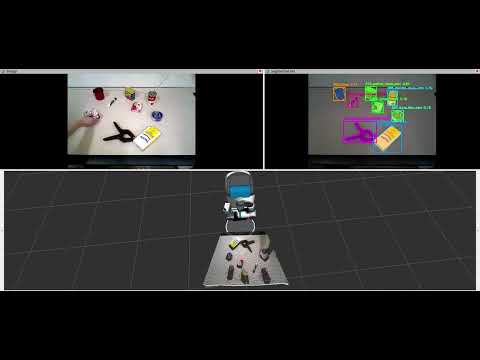
Click the following image ro this YouTube link to watch the video.
# add some packages for ROS
# Assume you are using ROS Noetic
conda install -c conda-forge rospkg empy
source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash
pip install rosnumpy
pip install easydict
pip install transforms3d
# test NIDS-Net on a YCBV image
python ros/test_ycb_sample.py
# use the ROS node to test NIDS-Net on YCBV objects
# Assume you are using GPU:0.
# This node is publishing the detection results for YCBV objects.
python ros/test_images_segmentation_NIDS_Net.py
# for visualization
cd ros
rosrun rviz rviz -d segmentation.rviz If you find the method useful in your research, please consider citing:
@misc{lu2024adapting,
title={Adapting Pre-Trained Vision Models for Novel Instance Detection and Segmentation},
author={Yangxiao Lu and Jishnu Jaykumar P and Yunhui Guo and Nicholas Ruozzi and Yu Xiang},
year={2024},
eprint={2405.17859},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}This project is based on the following repositories: