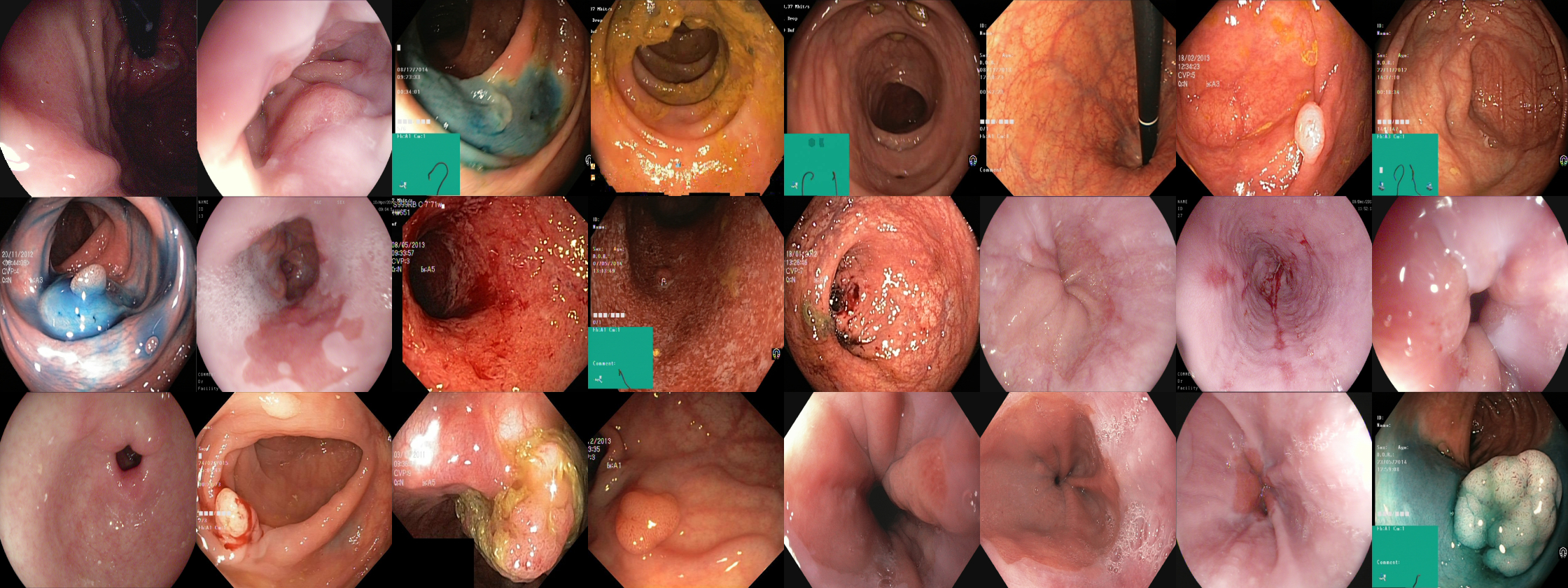
Medical image segmentation is a topic that has garnered a lot of attention over the last few years. Compared to classification and object detection, segmentation gives a more precise region of interest for a given class. This is immensely useful for the doctors as it not only specifies that an image contains something interesting but also where to look at which also provides some kind of inherent explanation. Colonoscopies are a perfect use-case for medical image segmentation as they contain a great variety of different findings that may be easily overlooked during the procedure.
Furthermore, transparent and interpretable machine learning systems are important to explain the whys and the hows of the predictions. This is especially important in medicine, where conclusions based on wrong decisions resulted from either biased or incorrect data, faulty evaluation or simply a bad model could be fatal. Therefore, the MedAI: Transparency in Medical Image Segmentation task aims to develop automatic segmentation systems that are transparent and explainable.
We present three subtasks; the polyp segmentation task, the instrument segmentation task, and the transparency task. Each task targets a different requirement within automatic findings segmentation in gastrointestinal image analysis. The participants are encouraged to submit to all subtasks, but it is not a requirement.
The polyp segmentation task asks participants to develop algorithms for segmenting polyps in images taken from endoscopies. The main focus of this task is to achieve high segmentation metrics on the supplied test dataset. Since last year, we have extended the development dataset and created a new testing dataset to which the submissions will be evaluated on.
Similar to the polyp segmentation task, the instrument segmentation task asks participants to develop algorithms for segmenting instruments present in colonoscopy videos. The main focus of this task is to achieve high segmentation metrics on the supplied test dataset.
The transparency task tries to measure the transparency of the systems used for the aforementioned segmentation tasks. The main focus for this task is to evaluate systems from a transparency point of view, meaning for example explanations of how the model was trained, the data that was used, and interpretation of a model's predictions.
We provide the participants with two open image segmentation datasets, one for polyp segmentation and one for gastrointestinal instrument segmentation. The datasets are split between a development part and a testing part, where the testing part will be held secret until after the challenge has ended. Both datasets were collected from real colonoscopies performed at Bærum Hospital, Vestre Viken Hospital Trust in Norway, and the annotations were verified by expert gastroenterologists (clinicians). The development end testing datasets can be downloaded below
The development dataset consists of 1,360 images of polyps with corresponding segmentation masks. Note that the dataset is based on HyperKvasr, a large public dataset contrainig diverse visual content from the gastrointestinal tract. Below you will find a link to the development dataset and HyperKvasir.
The development dataset consists of 300 images of polyps and 300 images of instruments. The ground truth masks are currently private but will be released after the competition ends.
The repository contains two jupyter notebooks (in the notebooks directory) aimed at giving you a starting point for the polyp and instrument segmentation tasks. As a baseline model we have provided a Unet build with Keras. Finally, we run the model inside a 10-fold cross-validation loop and we encourage the participants to also use som kind of resampling methods when reporting the results on the development set in the final paper to Nordic Machine Intelligence.
Each task will be evaluated using appropriate metrics. Overall, there will be one first place and one second place winner of MedAI, where the choice will be determined based on a combination of the evaluations gathered from each task.
The submitted segmentation masks for the polyp segmentation task and the instrument segmentation task will be assessed using standard evaluation metrics commonly used for segmentation tasks. This includes pixel accuracy, precision, recall, the Dice coefficient, and intersection over union (IoU). Different metrics tell different stories about the performance of a model under specific conditions, which is why we use multiple metrics to evaluate the submissions. The metric which will be used to rank submissions will be the IoU. Each team will receive a .csv file containing the aforementioned metrics.
The script used to evaluate all segmentation submissions can be found in the evaluation directory in this repository.
Submissions to the transparency task will be evaluated using a more qualitative approach compared to segmentation evaluations. A multi-disciplinary team will assess each submission that evaluates the transparency and understandability of the provided solutions. In this context, transparency will be measured by attributes like code availability, the thoroughness of the evaluation, and reproducibility. Each team will receive a report on the transparency of their solution, which will detail what parts were good and what parts may need more clarity.
The first and second place winners of the challenge will be awared with the following prizes. Note that you must complete all three tasks in order to be eligable for the prizes.
- First Prize: 5,000 Euro
- Second Prize: 2,500 Euro
The winning team will be announced during the Nordic AI Meet 2021 hosted on the 1-2nd of November at the Oslo Kongressenter.
| 5 August, 2021 | Development dataset release |
| 23 September, 2021 | Test dataset release |
| 27 September, 2021 | Participants submission of results |
| 8 October, 2021 | Evaluation results for participants |
| 15 October, 2021 | Methods description paper submission |
- Steven Hicks, SimulaMet, Norway steven (at) simula.no
- Debesh Jha, SimulaMet, Norway debesh (at) simula.no
- Vajira Thambawita, SimulaMet and OsloMet, Norway
- Pål Halvorsen, SimulaMet and OsloMet, Norway
- Bjørn-Jostein Singstad, Oslo University Hospital, Norway
- Sachin Gaur, University of Agder, Norway
- Klas H. Pettersen, NORA, Norway
- Morten Goodwin, University of Oslo, Norway
- Sravanthi Parasa, Swedish Medical Center, Sweden
- Thomas de Lange, Bærum Hospital, Norway
- Michael Riegler, SimulaMet, Norway